Criticism of the Book of Abraham
| Part of a series on the |
| Pearl of Great Price |
|---|
 |

The Book of Abraham is a work produced between 1835 and 1842 by the Latter Day Saints (LDS) movement founder Joseph Smith that he said was based on Egyptian papyri purchased from a traveling mummy exhibition. According to Smith, the book was "a translation of some ancient records ... purporting to be the writings of Abraham, while he was in Egypt, called the Book of Abraham, written by his own hand, upon papyrus".[1] The work was first published in 1842 and today is a canonical part of the Pearl of Great Price. Since its printing, the Book of Abraham has been a source of controversy. Numerous non-LDS Egyptologists, beginning in the mid-19th century, have heavily criticized Joseph Smith's translation and explanations of the facsimiles, unanimously concluding that his interpretations are inaccurate. They have also asserted that missing portions of the facsimiles were reconstructed incorrectly by Smith.
The controversy intensified in the late 1960s when portions of the Joseph Smith Papyri were located. Translations of the papyri revealed the rediscovered portions bore no relation to the Book of Abraham text. LDS apologist Hugh Nibley and Brigham Young University Egyptologists John L. Gee and Michael D. Rhodes subsequently offered detailed rebuttals to some criticisms. University of Chicago Egyptologist Robert K. Ritner concluded in 2014 that the source of the Book of Abraham "is the 'Breathing Permit of Hôr,' misunderstood and mistranslated by Joseph Smith."[2] He later said the Book of Abraham is now "confirmed as a perhaps well-meaning, but erroneous invention by Joseph Smith," and "despite its inauthenticity as a genuine historical narrative, the Book of Abraham remains a valuable witness to early American religious history and to the recourse to ancient texts as sources of modern religious faith and speculation."[2]
Background
[edit]
The Book of Abraham is an 1842 work produced by Latter Day Saints (LDS) movement founder Joseph Smith[3] that he claimed were translated from Egyptian papyri purchased from a traveling mummy exhibition. According to Smith, the book comprised "ancient records ... purporting to be the writings of Abraham, while he was in Egypt, called the Book of Abraham, written by his own hand, upon papyrus".[1] The book has five chapters,[4] and is often accompanied by three "facsimiles", or reproductions of vignettes which were copied from the original papyri.[5][6] According to Smith's explanations, Facsimile No. 1 depicts Abraham bound to a sacrificial altar, with the "idolatrous priest of Elkenah" looming over him with a knife;[7] Facsimile No. 2 is a circular depiction of the heavens (featuring planets, stars, the sun and moon, and other celestial objects) that also contains the grand key-words of the holy priesthood;[8] and Facsimile No. 3 portrays Abraham in the court of Pharaoh "reasoning upon the principles of Astronomy".[9]
The Book of Abraham text is a source for a number of distinct Latter Day Saint doctrines, which Mormon author Randal S. Chase calls "truths of the gospel of Jesus Christ that were previously unknown to Church members of Joseph Smith's day."[10] Examples include the nature of the priesthood,[11] an understanding of the cosmos,[12] the exaltation of humanity,[13] pre-mortal existence and the first and second estates,[14] and the plurality of gods.[15]
Joseph Smith papyri and Kirtland Egyptian papers
[edit]Sometime between 1817 and 1822, several Ptolemaic era fragments of papyri and eleven mummies were discovered by Antonio Lebolo in the ancient Egyptian city of Thebes. By the summer of 1835 they had made their way into the possession of Michael Chandler, who displayed them in Kirtland, Ohio, which at the time was the home of the Latter Day Saints, led by Joseph Smith. In 1830 Smith published a religious text called the Book of Mormon, which he said he translated from writings inscribed on golden plates written in what the book calls "reformed Egyptian".[16][17][18] Chandler advertised his antiquities with a "certificate of the learned" created while the mummies were displayed in the Philadelphia Arcade. After examining his artifacts, a group of scholars signed a promotional leaflet stating that the mummies "may have lived in the days of Jacob, Moses, or David...History records the fact, that the higher class concealed their knowledge from the lower, in figures and hieroglyphic characters...The papyrus, covered with black or red ink, or paint, in excellent preservation, are very interesting."[16] When Smith examined the scrolls, he said that they contained the writings of Abraham and Joseph (as well as a story about an "Egyptian princess" named "Katumin" or "Kah tou mun").[19][20] The four mummies and papyrus documents were purchased by Smith and a few others, and Smith with the help of scribes W.W. Phelps and Oliver Cowdery "commenced the translation of some of the characters or hieroglyphics."[21] By mid-July Phelps, Smith, and Cowdery began "translating an alphabet to the Book of Abraham, and arranging a grammar of the Egyptian language as practiced by the ancients."[22][23][24]

The collection of manuscripts Smith and his scribes produced is now known as the Kirtland Egyptian papers.[24][25] One of the manuscripts in this collection was a bound book simply titled "Grammar & A[l]phabet of the Egyptian Language" (GAEL), which contained Smith's interpretations of the Egyptian glyphs.[26][25] This manuscript details Smith's belief that hieroglyphics had five "degrees" of interpretation, with each "degree" representing a deeper, expanded, and more complex level of interpretation.[27] This manuscript illustrates Smith's method for translating the papyri: The scribes sketched out the hieroglyphic characters from the papyri onto the left-hand side of the manuscript. Smith then gave his English translation of the glyph, along with an explanation for how one would pronounce the character.[27]
Smith believed and taught that the papyri had been written by Biblical patriarchs themselves, and not by a later Egyptian scribe or a Jewish redactor.[28] In the article "Truth Will Prevail" published in the Latter Day Saint movement newspaper Times and Seasons, Smith wrote, "The Book of Abraham [was] written by his [i.e. Abraham's] own hand, upon papyrus".[1] Josiah Quincy said that upon a meeting with Smith, "some parchments inscribed with hieroglyphics were then offered us. They were preserved under glass and handled with great respect. 'That is the handwriting of Abraham, the father of the Faithful,' said the prophet."[28]
Smith began the translation of the Book of Abraham as early as July 1835, and completed through Abraham 2:19 by the end of that year. The rest was most likely completed in early 1842.[29][30] When translating the book, Smith dictated, and Warren Parrish, Phelps, and Frederick G. Williams served as his scribes.[31] The complete work was first published serially in Times and Seasons in 1842,[a] and it was later canonized in 1880 by the LDS Church as part of its Pearl of Great Price.[3]
The papyrus and mummies were presumed lost in the Great Chicago Fire in 1871, but 11 sections of the papyri were rediscovered in the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art in 1966 and acquired by the LDS Church.[33][34][35] Three of these fragments were designated Joseph Smith Papyri (JSP) I, X, and XI.[36] Other fragments, designated JSP II, IV, V, VI, VII, and VIII, are thought by critics to be the Book of Joseph to which Smith referred when first examining the text.[37] A twelfth fragment was discovered in the LDS Church Historian's office and was dubbed the "Church Historian's Fragment". Disclosed by the church in 1968, the fragment was designated JSP IX by scholars.[38] Although there is some debate about how much of the papyrus collection is missing, there is broad agreement that the recovered papyri are indeed portions of Smith's original purchase, partly based on the fact that they were pasted onto paper which had "drawings of a temple and maps of the Kirtland, Ohio area" on the back, as well as the fact that they were accompanied by an affidavit by Emma Smith, stating that they had been in the possession of Joseph Smith.[39]
Analysis and translation of the papyrus by Egyptologists
[edit]
In November 1967, the LDS Church asked Hugh Nibley, a professor of ancient scripture at Brigham Young University (BYU), to study the fragments. Although competent in numerous languages, Nibley did not have a working knowledge of the ancient Egyptian script or language at the time, so he studied under the University of Chicago professor John A. Wilson so that he could translate the papyri himself.[40]
The LDS Church published sepia photographs of the papyri in its magazine Improvement Era in February 1968. Although a translation was not provided by the church at this time,[41][42][43] soon thereafter the editors of an independent quarterly journal Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought published their own translation after consulting with several Egyptologists and scholars, including: Klaus Baer, a researcher at the University of Chicago's Oriental Institute; Richard Anthony Parker, the Director of the Department of Egyptology at Brown University; Jerald Tanner, an independent scholar; and John A. Wilson, the director of the Oriental Institute.[41][44][45][46] Since 1968, numerous other translations have also been published by Mormon and non-Mormon scholars, including Michael D. Rhodes (BYU),[47] John Gee (BYU),[48] and Robert K. Ritner (University of Chicago).[49]
The translation by both Mormon and non-Mormon Egyptologists is completely at odds with Joseph Smith's purported translation.[50] The transliterated text from the recovered papyri and facsimiles published in the Book of Abraham contain no direct references—either historical or textual—to Abraham at all,[51][52] and the patriarch's name does not appear anywhere on the papyri or the facsimiles. Edward Ashment notes, "The sign that Smith identified with Abraham ... is nothing more than the hieratic version of ... a 'w' in Egyptian. It has no phonetic or semantic relationship to [Smith's] 'Ah-broam.'"[52] BYU scholar Michael Rhodes summarized the content of the papyri as follows:
The Hor Book of Breathings" is a part of eleven papyri fragments ... from three separate papyri scrolls. Joseph Smith Papyri I, X, and XI are from the Book of Breathings belonging to Hor (Hr) the son of Usirwer. Joseph Smith Papyri II, IV, V, VI, VII, and IX all came from a Book of the Dead belonging to Tshemmim (Ts-sri.t Min.), the daughter of Eskhons (Ns-Hnsw). Finally, Joseph Smith Papyrus III is part of Chapter 125 of the Book of the Dead belonging to Neferirtnub (Nfr-ir(.t)-nbw).[53]
Examining JSP I, Egyptologist Klaus Baer translated the writing on the right of the vignette as follows:
[T]he prophet of Amonrasonter, prophet [?] of Min Bull-of-his-Mother, prophet [?] of Khons the Governor ... Hor, justified, son of the holder of the same titles, master of secrets, and purifier of the gods Osorwer, justified [?] ... Tikhebyt, justified. May your ba live among them, and may you be buried in the West ... May you give him a good, splendid burial on the West of Thebes just like ...[54]
The hieratic text found to the left of the vignette (i.e. the "Small Sensen" text) on JSP I was initially translated by Parker. His translation is as follows:
[T]his great pool of Khonsu [Osiris Hor, justified], born of Taykhebyt, a man likewise. After (his) two arms are [fast]ened to his breast, one wraps the Book of Breathings, which is with writing both inside and outside of it, with royal linen, it being placed (at) his left arm near his heart, this having been done at his wrapping and outside it. If this book be recited for him, then he will breathe like the soul[s of the gods] for ever and ever.[55]
Scholars have dated the Joseph Smith Papyri to the late Ptolemaic period (c. 150 BC), 1500 years after Abraham's supposed lifetime.[51][56][57][58][59] This fact—combined with the presence of apparent anachronisms within the book itself[b]—seems to contradict Smith's statements that the papyri feature the "handwriting of Abraham" which had been "written by his own hand".[61]
Sources
[edit]Egyptologists have concluded that the papyri fragments were originally part of the following sources:
| Fragment no.[62] | Egyptian source[63] | Composition date[64] | Status[65] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joseph Smith Papyri (JSP): I (source of Facsimile No. 1), part of IV, X, XI | "Book of Breathing", papyrus of Hôr | c. 150 BC | Owned by the LDS Church |
| JSP: II, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX | "Book of the Dead", papyrus of Ta-sherit-Min | After 500 BC | Owned by the LDS Church |
| JSP: III a–b | "Book of the Dead", papyrus of Nefer-ir-nebu | After 500 BC | Owned by the LDS Church |
| Source of Facsimile No. 2 | Hypocephalus of Sheshonq | Unknown | Presumed lost in the Great Chicago Fire; reproduction of the Hypocephalus of Sheshonq included in the Kirtland Egyptian papers |
| Source of Facsimile No. 3 | "Book of Breathing", papyrus of Hôr | c. 150 BC | Presumed lost in the Great Chicago Fire |
Manuscript-based criticism
[edit]The "Egyptian Alphabet and Grammar"
[edit]
Several criticisms of the Book of Abraham have been brought forth that hinge on evidence found in the "Egyptian Alphabet and Grammar". One such argument focuses on the aforementioned document and its connection to Joseph Smith Papyrus XI, also known as the "Small Sensen" papyrus (i.e. the small scrap of papyrus attached to left side of JSP I).[66] Several pages in the "Egyptian Alphabet and Grammar" contain an arrangement of correlated characters from the Small Sensen papyrus. These pages are divided into two halves: on the left-hand side of a given page, Egyptian characters are listed, and on the right side, an apparent translation of these characters is given.[27][67] This suggests that whoever created the correlation was attempting to perform a direct, literal, and comprehensive translation (as opposed to a merely spiritual or divined translation, as some apologists contend) of the figures of the papyri scraps.[28]
While the "Egyptian Alphabet and Grammar" only contains an explicit correlation between Egyptian characters[c] and their purported English translation for Abraham 1:11–2:9, the document itself suggests that the hieroglyphs from the Small Sensen papyrus were used to translate much of the Book of Abraham.[66] This is supported by a quote from James Ratcliffe Clark, the author of the 1955 book the Story of the Pearl of Great Price, who wrote: "I have in my possession a photostatic copy of the manuscript of the Prophet Joseph Smith's translation of Abraham 1:1 to 2:18. ... The characters from which our present Book of Abraham was translated are down to the left-hand column and Joseph Smith's translation opposite, so we know approximately how much material was translated from each character."[69]
This correlation found in the "Egyptian Alphabet and Grammar" between Abraham 1:11–2:9 and the Small Sensen papyrus has thus led many critics to assert that all of the Book of Abraham text came entirely from Smith's interpretation of the Small Sensen papyrus, rather than a hypothetical lost section (as is often asserted by apologists).[66][70] This means, however, that Smith would have used a single Egyptian character to derive dozens of words, as Jerald Tanner notes: "Joseph Smith apparently translated many English words from each Egyptian character. The characters from fewer than four lines of the papyrus make up forty-nine verses of the Book of Abraham, containing more than two thousand words. If Joseph Smith continued to translate the same number of English words from each Egyptian character, this one small fragment would complete the entire text of the Book of Abraham. In other words, the small piece of papyrus [i.e. the fragment known as Fragment XI] appears to be the whole Book of Abraham!"[69]
The facsimiles
[edit]Early criticism of the facsimiles
[edit]In 1856, Gustav Seyffarth viewed the Joseph Smith Papyri at the St. Louis Museum, making the following statement regarding them: "The papyrus roll is not a record but an invocation to the Deity Osirus [sic], in which occurs the name of the person, and a picture of the attendant spirits, introducing the dead to the Judge, Osiris."[71] Later that same year, a pamphlet containing the Book of Abraham's facsimiles was sent to the Louvre. Here, Theodule Deveria, an Egyptologist at the museum, had the opportunity to examine the facsimiles, which he recognized as "common Egyptian funerary documents, of which he had examined hundreds."[72] He argued that many of the hieroglyphic characters had been poorly transcribed and that several areas in the facsimiles seemed to have been reconstructed based on guesswork. Deveria consequently concluded that Joseph Smith's explanation was "rambling nonsense".[72] Despite this condemnation, the LDS Church did not respond to Deveria's critiques at the time.[73] Then, in 1873, Deveria's interpretation, juxtaposed with Smith's interpretation, was published in T. B. H. Stenhouse's book The Rocky Mountain Saints: A Full and Complete History of the Mormons, a work critical of the LDS Church.[74] This time, the church responded by reiterating that the Book of Mormon was divinely inspired, and that the Book of Abraham's source papyri had "two meanings" (one that was obvious and easily understood by a lay audience, and another that was more esoteric and only accessible to the priesthood). In 1880, the Book of Abraham was officially canonized by the Church.[75]
Several decades later, in 1912, Episcopal Bishop Franklin S. Spalding sent copies of the three facsimiles to eight Egyptologists, semitists, Christian theologians, and historians,[d] soliciting their interpretation of the facsimiles; the results were published in a pamphlet entitled, Joseph Smith, Jr. as a Translator: An Inquiry. The eight scholars wrote that the images were taken from standard funerary documents, and some of the scholars even harshly criticized Smith's interpretation.[77] Egyptologist James H. Breasted of the University of Chicago, for instance, noted: "[T]hese three facsimiles of Egyptian documents in the 'Pearl of Great Price' depict the most common objects in the Mortuary religion of Egypt. Joseph Smith's interpretations of them as part of a unique revelation through Abraham, therefore, very clearly demonstrates that he was totally unacquainted with the significance of these documents and absolutely ignorant of the simplest facts of Egyptian writing and civilization."[78] Flinders Petrie of London University wrote: "It may be safely said that there is not one single word that is true in these explanations".[79] Finally, Archibald Sayce, Oxford professor of Egyptology, stated: "It is difficult to deal seriously with Joseph Smith's impudent fraud ... Smith has turned the goddess [Isis in Facsimile No. 3] into a king and Osiris into Abraham."[80]
Once again, the LDS Church defended the legitimacy of the book, this time by arguing that these scholars were employing improper methods and faulty reasoning. LDS apologists argued that, because many of the Egyptian experts had pointed out that the facsimiles were reminiscent of similar documents, or that certain areas on the facsimiles appeared different from known funerary texts, these scholars were merely ignoring potentially key differences in the facsimiles so that their arguments might seem effective. Such a line of reasoning is exemplified by a note written by Church historian B. H. Roberts: "Yes, or some other change might be suggested, and by such a process some other meaning may be read into the place and make it different from the translation of Joseph Smith."[81] The Church eventually hired an individual named Robert C. Webb (the pen name of J. E. Homans), to defend the veracity of the Book of Abraham. In his 1915 work The Case Against Mormonism (in which he claimed to have a PhD, despite this being a lie), he collected several interpretations of Facsimile No. 1 from Egyptologists that sounded unrelated to the layperson (i.e. that the facsimile represented: "an embalming", "the Resurrection of Osiris", or "Anubis guarding the embalmed mummy") and claimed: "If any of these Egyptologists is right, therefore, this drawing must have been radically altered in several essential particulars. In view of their disagreements, it will be necessary to demonstrate any conclusions drawn. Will some learned person be pleased to tell us what this scene represents? Otherwise, how can we condemn Joseph Smith for 'fraud'...?"[82]
Facsimile No. 1
[edit]Joseph Smith claimed that Facsimile No. 1 portrays Abraham on an altar, about to be sacrificed by an "idolatrous priest of Elkenah".[7] The Book of Abraham makes explicit reference to this facsimile, noting: "That you may have a knowledge of this altar, I will refer you to the representation at the commencement of this record."[83][84] Egyptologists, however, point out that it is a vignette taken from a version of The Book of Breathings,[85][86][87][88] also known as the "Breathing Permit",[56] copied for a Theban priest named Hôr.[89][e] A comparison of Smith's interpretation of the facsimile, and that of Egyptologists is as follows:
| Figure | Joseph Smith's explanation[91] | Explanation by Egyptologists |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The Angel of the Lord. | "The ba-spirit Osiris, miscopied with the head of a bird rather than that of a human"[92] |
| 2 | Abraham fastened upon an altar. | "The prone image of Osiris"[93] |
| 3 | The idolatrous priest of Elkenah attempting to offer up Abraham as a sacrifice. | "The jackal-headed Anubis, god of mummification, extending his hand to ensure the resurrection of the mummy of the deceased Osiris ... Although most of Anubis' head is now missing, the back of his wig still appears above his shoulder and his dark skin is evident"[94] |
| 4 | The altar for sacrifice by the idolatrous priests, standing before the gods of Elkenah [sic], Libnah, Mahmackrah, Korash, and Pharaoh. | "the customary lion-headed funerary bier"[94] |
| 5 | The idolatrous god of Elkenah. | One of "the four 'canopic jars' [representing] falcon-headed Qebehsenuf, protector of the intestines"[95] |
| 6 | The idolatrous god of Libnah. | "One of "the four 'canopic jars' [representing] jackal-headed Duamutef, protector of the stomach"[95] |
| 7 | The idolatrous god of Mahmackrah. | "One of "the four 'canopic jars' [representing] baboon-headed Hapi, protector of the lungs"[95] |
| 8 | The idolatrous god of Korash. | "One of "the four 'canopic jars' [representing] human-headed Imseti, protector of the liver"[95] |
| 9 | The idolatrous god of Pharaoh. | "The crocodile who aided in the collection of the dismembered limbs of Osiris"[96] |
| 10 | Abraham in Egypt. | "A typical offering stand with a spouted vessel and Nile water lily flowers"[96] |
| 11 | Designed to represent the pillars of heaven, as understood by the Egyptians. | "A 'niched-brick' facade, originally an architectural feature ... that became an artistic convention for the decoration of the dado of sacred wall scenes"[96] |
| 12 | Raukeeyang, signifying expanse, or the firmament over our heads; but in this case, in relation to this subject, the Egyptians meant it to signify Shaumau, to be high, or the heavens, answering to the Hebrew word, Shaumahyeem. | "A stream of Nile water (show by hatched lines)";[96] "The word Shauman [sic] is not Egyptian, and the Hebrew word שָׁמַ֫יִם [i.e. shamayim] is badly copied)"[74] |
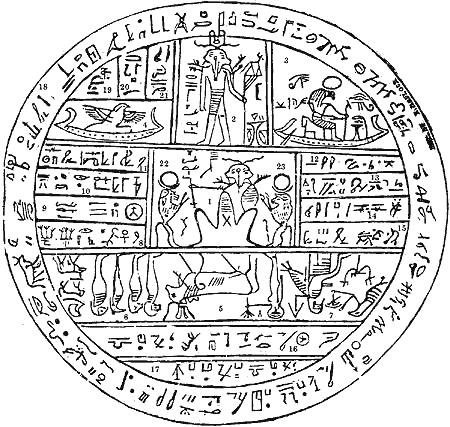
Facsimile No. 2
[edit]Joseph Smith claimed that Facsimile No. 2 was a representations of celestial objects.[8] Egyptologists, however, argue that the figure represented by Facsimile No. 2 is a common Egyptian artifact called a hypocephalus. Hypocephali were placed under the head or feet of the mummified person to magically protect the deceased, causing the head and body to be enveloped in light and warmth.[97] The hypocephalus in question was prepared for an individual named Sheshonq.[98] A comparison of Smith's interpretation of the facsimile, and that of Egyptologists is as follows:
| Figure | Joseph Smith's explanation[99] | Explanation by Egyptologists |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kolob, signifying the first creation, nearest to the celestial, or the residence of God. First in government, the last pertaining to the measurement of time. The measurement according to celestial time, which celestial time signifies one day to a cubit. One day in Kolob is equal to a thousand years according to the measurement of this earth, which is called by the Egyptians Jah-oh-eh. | "In the center field, a seated figure of Re-Atum (originally with four ram heads and complex crown and scepters) is worshipped by two apes crowned with lunar disks ... Smith simply copied the heads and shoulders (with jackal extensions) of the double headed god in the upper register ... The equation of a day to a cubit is specious, and the Egyptian terms for earth do not include ... Jah-oh-eh";[100] "The word Jah-oh-eh has nothing Egyptian in it; it resembles the Hebrew word יהוה [i.e. the Tetragrammaton] badly transcribed."[74][101] |
| 2 | Stands next to Kolob, called by the Egyptians Oliblish, which is the next grand governing creation near to the celestial or the place where God resides; holding the key of power also, pertaining to other planets; as revealed from God to Abraham, as he offered sacrifice upon an altar, which he had built unto the Lord. | "A two-headed deity strides with the standard of the god Wepwawet ... The god wears a crown of double-plumes and sun-disk over horizontal horns, and jackal heads protrude from both of his shoulders. [The images] to the right of this figure [and] the altar of Facsimile 2 [are] a fabrication by Smith. ... Smith's interpretation of the deity as being 'called by the Egyptians Oliblish' is nonsense".[102] |
| 3 | Is made to represent God, sitting upon his throne, clothed with power and authority; with a crown of eternal light upon his head; representing also the grand Key-words of the Holy Priesthood, as revealed to Adam in the Garden of Eden, as also to Seth, Noah, Melchizedek, Abraham, and all to whom the Priesthood was revealed. | "The sun god Ra, with a hawk's head, seated in his boat. In the field the two symbolical figuring, according to M. de Rougé, the fixed points of an astronomical period."[74][101] |
| 4 | Answers to the Hebrew word Raukeeyang, signifying expanse, or the firmament of the heavens; also a numerical figure, in Egyptian signifying one thousand; answering to the measuring of the time of Oliblish, which is equal with Kolob in its revolution and in its measuring of time. | "A standard image of the mummiform god Sokar in his barque";[103] "The Hebrew word רָקִיעַ, [i.e. raqiya, the firmament], besides being badly described, has no relation whatever to this figure".[74][101] |
| 5 | Is called in Egyptian Enish-go-on-dosh; this is one of the governing planets also, and is said by the Egyptians to be the Sun, and to borrow its light from Kolob through the medium of Kae-e-vanrash, which is the grand Key, or, in other words, the governing power, which governs fifteen other fixed planets or stars, as also Floeese or the Moon, the Earth and the Sun in their annual revolutions. This planet receives its power through the medium of Kli-flos-is-es, or Hah-ko-kau-beam". | "Hathor [the] heavenly cow strides in the center, followed by a goddess whose head is a disk with the Wedjat-Eye and who extends a water lily."[104] |
| 6 | Represents this earth in its four quarters. | "Before the Hathor cow stand the mummiform sons of Horus [i.e. Amset, Hapy, Tioumautew, and Kebhsoniw] and a trigram for the sun god in his three manifestations".[74][101][105] |
| 7 | Represents God sitting upon his throne, revealing through the heavens the grand Key-words of the Priesthood; as, also, the sign of the Holy Ghost unto Abraham, in the form of a dove. | "Behind (and facing away from) Hathor and the goddess appears the enthroned and ithyphallic Min-Amon, in half human and half bird form, raising his arm with a flabellum. The ithyphallic serpent deity Nehebkau stands before Min-Amon, offering the Wedjat-Eye."[105] |
| 8 | Contains writings that cannot be revealed unto the world; but is to be had in the Holy Temple of God. | Text reading: "O noble god from the beginning of time, great god, lord of heaven, earth, underworld, waters [and mountains], cause the ba-spirit of the Osiris Sheshonq to live."[106] |
| 9 | Ought not to be revealed at the present time. | |
| 10 | Also. | |
| 11 | Also. If the world can find out these numbers, so let it be. Amen. | |
| 12 | Will be given in the own due time of the Lord. | Upside down Hieratic text reading: "near" and "wrap"[107] |
| 13 | Upside down Hieratic text reading: "which made by"[107] | |
| 14 | Upside down Hieratic text reading: "breathings"[107] | |
| 15 | Upside down Hieratic text reading: "this book";[107] hieroglyphic text reading, "his words"[108] | |
| 16, 17 | Text reading: "May this tomb never be desecrated, and may this soul and its lord never be desecrated in the hereafter."[109] | |
| 18 | Text reading: "I am the punisher in the Mansion of the Benben in Heliopolis, greatly exalted, greatly [effective], the copulating bull who has no equal, this great god in the Mansion of the Benben in Heliopolis, ... Come to the Osiris Shesonq, the justified son of ... He is that great god in the House of the Noble."[110] | |
| 19, 20, and 21 | Text reading: "You shall be as that god, the Busirian."[108] | |
| 22, 23 | "Kli-flos-is-es [and] Hah-ko-kau-beam [which are] stars [that receive] light from the revolutions of Kolob." | "Two apes ... with horned moon-disks on their heads, in an attitude of adoration."[111] |
| Conclusion | The above translation is given as far as we have any right to give at the present time. | "It is evident to me that several of the figures to be found in these various MSS. have been intentionally altered."[74][101] |
Facsimile No. 3
[edit]Joseph Smith interpreted Facsimile No. 3 as representing Abraham sitting on the Pharaoh's throne teaching the principles of astronomy to the Egyptian court.[9] Egyptologists, however, interpret this as a scene from the 125th chapter of The Book of the Dead, in which the deceased person for whom the scroll was made is presented before the Egyptian god Osiris. Surrounding Hôr and Osiris are the goddess Maat, the god Anubis, and the goddess Isis.[112] Hieroglyphics at the bottom of the scroll identify Hôr, the deceased.[113] It is likely that this vignette appeared at the end of the same papyrus scroll that featured the vignette which served as the basis for Facsimile No. 1.[113] A comparison of Smith's interpretation of the facsimile, and that of Egyptologists is as follows:
| Figure | Joseph Smith's explanation[114] | Egyptological explanation |
|---|---|---|
| General Comment | Abraham is reasoning upon the principles of Astronomy, in the king's court. | "Invocation (text at bottom line below the illustration): O gods of the necropolis, gods of the caverns, gods of the south, north, west, and east grant salvation to the Osiris Hor, the justified, born by Taikhibit."[115] |
| 1 | Abraham sitting upon Pharaoh's throne, by the politeness of the king, with a crown upon his head, representing the Priesthood, as emblematical of the grand Presidency in Heaven; with the scepter of justice and judgment in his hand. | "Label for Osiris (text to the right of figure 1 of Facsimile No. 3): Recitation by Osiris, Foremost of the Westerners, Lord of Abydos(?), the great god forever and ever(?)."[115] |
| 2 | King Pharaoh, whose name is given in the characters above his head. | "Label for Isis (text to the right of figure 2 of Facsimile No. 3): Isis the great, the god's mother."[115] |
| 3 | Signifies Abraham in Egypt as given also in figure 10 of Facsimile No. 1. | "Altar, with the offering of the deceased, surrounded with lotus flowers, signifying the offering of the defunct."[74] |
| 4 | Prince of Pharaoh, King of Egypt, as written above the hand. | "Label for Maat (text to the left of figure 4 of Facsimile No. 3): Maat, mistress of the gods."[115] |
| 5 | Shulem, one of the king's principal waiters, as represented by the characters above his hand. | "Label for Hor the deceased (text in front of figure 5 of Facsimile No. 3): The Osiris Hor, justified forever."[115] |
| 6 | Olimlah, a slave belonging to the prince. | "Label for Anubis (text in front of figure 6 of Facsimile No. 3): Recitation by Anubis, who makes protection(?), foremost of the embalming booth ..."[115] |
Questionable reconstruction of lacunae
[edit]
Several Egyptologists, including Deveria, Klaus Baer, Richard Anthony Parker, and Albert Lythgoe noted that portions of Facsimile No. 1 appeared to be incorrectly depicted—based on comparison with other similar Egyptian vignettes—and suspected that they had been reconstructed from lacunae (i.e. gaps) in the original papyri; Larson notes, "[S]ome elements in several of the drawings appeared to Deveria to be guesswork, probably incorrect restorations of missing sections of the original papyri."[72] Indeed, when the original papyri were later discovered, a comparison of the facsimiles with the papyri and the Kirtland Egyptian Papers revealed that the areas on Facsimile No. 1 which Egyptologists claim look modified (e.g. the heads of "the idolatrous priest" and the "angel of the Lord", the priest's knife) are the same sections that are missing from the extant fragment (i.e. Fragment I).[113][116] This lent credence to the Egyptologists' conclusions that Smith filled in these areas himself.[49][117][118][119]
Egyptologists have also criticized Facsimile No. 2 for containing false reconstruction of lacunae, suggesting that Smith reconstructed portions of the vignette with characters from another papyrus.[120] Critics note that an incomplete version of Facsimile No. 2 is found among the Kirtland Egyptian Papers, part of which are in Smith's handwriting. Comparing the published version of Facsimile No. 2 with the version from the Kirtland Egyptian Papers and the newly rediscovered papyri reveals that characters from a different papyrus fragment were used to fill in the missing portions of Facsimile No. 2.[120][121] Michael Rhodes notes:
A careful examination of Facsimile No. 2 shows that there is a difference between most of the hieroglyphic signs and the signs on the right third of the figure on the outer edge as well as the outer portions of the sections numbered 12–15. These signs are hieratic, not hieroglyphic, and are inverted, or upside down, to the rest of the text. In fact, they are a fairly accurate copy of lines 2, 3, and 4 of the Joseph Smith Papyrus XI, which contains a portion of the Book of Breathings. Especially clear is the word snsn, in section 14, and part of the name of the mother of the owner of the papyrus, (tay-)uby.t, repeated twice on the outer edge. An ink drawing of the hypocephalus in the Church Historian's office shows these same areas as being blank. It is likely that these portions were missing from the original hypocephalus and someone (e.g., the engraver, one of Joseph Smith's associates, or Joseph himself) copied the lines from the Book of Breathings papyrus for aesthetic purposes.[111]
Apologist responses to criticism of the facsimiles
[edit]Latter-day Saint Egyptologist John Gee, counters the idea that Smith reconstructed the lacunae by claiming that eyewitnesses of the papyri during Smith's lifetime described a complete document, free of lacunae. Thus, Gee argues that the facsimile is an accurate reproduction of an original document that has since suffered significant damage. Gee gives as an example "the man with a drawn knife", a portion that is no longer extant but was reported in both apologetic and critical writings of the time.[122]
Some apologists also believe that there are differences between the vignette and other comparable vignettes that render the standard interpretation incorrect.[f] Apologists have also challenged the Egyptologists' means of successfully interpreting the facsimiles, arguing that the papyrus had been written, not for future Egyptologists or even contemporary Egyptians, but rather for Egyptian Jews. These apologists contend that the papyri may have been created by a Jewish redactor, adapting Egyptian religious sources, but imbuing them with new Semitic religious context. Apologists give examples of such Jewish adaptations to help explain how the facsimiles can support Smith's possible translation of the book.[36][124] Mormon apologists also allege the assertion that Smith's reconstructions were flawed—an assertion that has been put forth by several Egyptologists—is mere speculation that fallaciously presupposes that the Egyptologist interpretation is correct. These apologists therefore assert that Smith's reconstruction was either correct, was done so as to make the images more aesthetically pleasing, or was inconsequential to the original interpretation of the Book of Abraham.[111][g]
Hugh Nibley of Brigham Young University notes that the seemingly misidentified characters in Facsimile No. 3 may have been participating in a ritual where both men and women can be represented by the opposite sex.[126] Nibley also argues that Smith's interpretation of the facsimile avoids making "romantic and quite unjustified conclusions" (e.g. identifying the seated person as Pharaoh, identifying the two feminine figures as Pharaoh's wife and daughter, or as Abraham's wife Sarah); instead, Nibley contends that Smith's interpretation of the facsimile is consistent with modern understandings of "the court scenes on other biographical or autobiographical records" (for instance, that the figure in the center of a stele is usually the owner or "usually some personal servant or palace officer attendant on Pharaoh", and that Smith indeed identified one of the central figure as a servant-cum-waiter named Shulem).[127]
Apologists also cite parallels between the scenes depicted on the facsimiles and several ancient documents and other Jewish writings, maintaining that there is no evidence that Smith studied or even had access to these sources. Examples include: the attempted sacrifice of Abraham and his subsequent rescue (a similar story was preserved in a Coptic encomium only translated into English in the 20th century),[128][129] Abraham teaching the Egyptians astronomy (this is recounted in the aforementioned Coptic encomium, and is mentioned by Eusebius, quoting Pseudo-Eupolemus, in his work Praeparatio evangelica),[129][130][131][h] and God teaching astronomy to Abraham.[133]
Historicity
[edit]The historicity of the Book of Abraham is not accepted by non-LDS scholars and by some LDS scholars. The existence of the patriarch Abraham is questioned even in the Biblical narrative by some researchers.[134] Various anachronism and 19th century themes lead scholars to conclude that the Book of Abraham is a 19th century creation.[2]
Anachronisms
[edit]Biblical scholars place Abraham living no later than 1500 BCE, making anything coming into existence after that time anachronistic.[135] LDS Church scholars either reject the anachronisms, or accept the anachronisms and attribute them to either Joseph Smith and/or an ancient Jewish redactor, who while copying from the original Book of Abraham replaced original terms and images with concepts that would be understandable to a contemporary audience.[136][137] This includes the facsimiles that are found in the Book of Abraham, which represent a corrupted version of a document originally written by Abraham, and Smith gave the interpretation of the original document.[138] In response to criticism that the documents are too young to have been written by Abraham, Nibley and others argue that the papyri may be copies of an original which was either written or commissioned personally by Abraham, and thus the copies could be considered "by [Abraham's] own hand" in the sense that they were derived from an original.[139] Critics of this approach point to repeated statements by Smith and others that the papyri he was translating from were literally written in the handwriting of Abraham and Joseph.[140][28]
Depiction of angels
[edit]In the Book of Abraham facsimile #1 and in Abraham 1:15, an angel is depicted as saving Abraham from being sacrificed. Biblical scholars argue that the concept of an "Angel" as benevolent semi-divine beings as portrayed in the Book of Abraham did not develop in Judaism until the post-exilic period.[141][142]
Documentary dependence
[edit]Biblical scholars agree that the book of Genesis is not a unified work from a single author, but is made up of Judean sources combined over many centuries by many hands, some of them over 1,000 years after Abraham.[143] The dependence of the creation account found in the Book of Abraham on these late sources render it anachronistic.[144]
Egyptus
[edit]The Book of Abraham states that Egypt was discovered by a daughter of Ham named "Egyptus, which in the Chaldean signifies Egypt, which signifies that which is forbidden. When this woman discovered the land it was under water, who afterward settled her sons in it." Her sons went on to become the Pharaohs of Egypt.[145] The word "Egyptus" is a Greek word, not Chaldean and means, "the house of the ka of Ptah" referring to the Temple of Ptah in Memphis. It does not mean "forbidden" in any language.[146]
Facsimile #2 (Hypocephalus)
[edit]Facsimile #2 is an Egyptian funerary document called a Hypocephalus. These objects, which were placed under the head of the deceased and symbolized the eye of a deity, first came into use c. 400–301 BC, well after Abraham would have lived.[140][147][148]
LDS Scholar Royal Skousen has argued that Smith made a mistake when he connected the facsimiles to the revealed text. For Skousen, sentences referencing the facsimiles were interlinear or margin notes that were not part of the actual revealed text. As such, he believes the facsimiles themselves are not part of the Book of Abraham and are extracanonical.[149]
Human sacrifice as an Egyptian religious practice
[edit]The Book of Abraham discusses men, women and children being sacrificed to Egyptian gods for religious reasons, such as a child as a thank offering.[150] The sacrifices were said to be done "after the manner of the Egyptians."[151]
Offering human sacrifice to Gods was not a religious practice of the ancient Egyptians.[152] LDS Egyptologist Kerry Muhlestein has argued that ritual killing did occur in ancient Egypt as punishment for religious dissent.[153][154] Critics of this approach argue that religious ritual surrounding political capital punishment is fundamentally different than ritual surrounding religious human sacrifices such as making thank offerings of children to Gods as depicted in the Book of Abraham.[152][155]
Pharaoh
[edit]The Book of Abraham uses the word Pharaoh as the proper name of the first Egyptian king that means "king by royal blood".[156] The word Pharaoh initially meant "great house" and was not used as a title for a King until around 1500 BC.[157]
Prophetic figure writing scripture
[edit]LDS Scholar David Bokovoy writes in arguing that the Book of Abraham should be read as inspired pseudepigrapha, "The notion of an ancient prophetic figure or patriarch writing scripture is historically anachronistic. Though traces of Moses as author exist in the Book of Deuteronomy, this view of scripture did not develop fully in Judean thought until the Hellenistic era (321–31BC)."[144]
Potiphar's Hill
[edit]The Book of Abraham says that Abraham was taken to be sacrificed at a place called "Potiphar's Hill".[158] The name "Potiphar" is of Late Egyptian origin and grammatical construction and means "the one whom Re has given" using a form of Re's name with the definite article ("Pre") that did not exist in Abraham's day.[159] The name is unknown before the 11th century BCE and is also considered anachronistic in the Bible.[146] Sumerologist Christopher Woods wrote that the name Potiphar "has no place linguistically or culturally in the toponymy of southern or northern Mesopotamia."[160]
Sephardic Hebrew
[edit]The Book of Abraham contains a number of Hebrew words, several of them with clear Sephardi Hebrew influence, a dialect that originated with Jews in medieval Europe.[161][162][163] Hebrew itself was not a written language until around the tenth century BCE.[144]
Ur of the Chaldees
[edit]The opening chapter of the Book of Abraham takes place in "land of Ur, of Chaldea".[156] The location of Ur has been debated by historians, however the qualifier of "Chaldea" firmly places Ur in southern Mesopotamia.[160][164] While fragments of Egyptian vessels and other items found indicate trade between Mesopotamia and Egypt, there is no evidence that Egyptian religion was ever practiced in either Northern or Southern Mesopotamia, or in any way displaced local religious traditions.[160] Additionally, the Chaldeans did not exist as a people until the 9th century BC—well after the purported time of Abraham.[135]
Arguments for historicity
[edit]Leiden papyrus
[edit]
In a 2013 essay on the Book of Abraham, the LDS Church argued for the historicity of the Book of Abraham by citing as evidence "a third-century papyrus from an Egyptian temple library [that] connects Abraham with an illustration similar to facsimile 1 in the book of Abraham."[130][165] The damaged papyrus written in Greek is a love spell designed to create feelings of passion in a woman. The broken text has been translated as:
...you bring a sealed ... of copper ... this lion, this mummy (?), and this Anubis ... while they seek ... black scarab (?) ... put ... "...AIDIO ORICH THAMBITO, Abraham who at ... PLANOIEGCHIBIOTH MOU and the whole soul for her, <person> [who <person> bore] ... the female body of her, <person> [whom <person> bore], I conjure by the ... [and] to inflame her, <person> whom [<person> bore]." [Write these] words together with this picture on a new papyrus:[166]
Critics have countered that the lion couch scene on the Leiden papyrus originated well after the Jewish diaspora when Jewish ideas were spread throughout the Mediterranean world, the word Abraham was commonly used in magic spells as an "abracadabra"-type magic word, and that the person on the lion couch scene is the woman who is the target of the passion spell, not Abraham.[2]
Literary dependence
[edit]King James Version of the Bible
[edit]The Book of Abraham contains a creation story similar to Genesis chapters 1 and 2. The Book of Abraham retains 75 percent of the wording of the King James Version of the Bible.[167] The creation account found in both the Book of Abraham and King James Version has a literary dependence on late Judean sources. The Book of Abraham in several places further combines two documents (the Priestly source and Jahwist source), indicating that the Book of Abraham depends on the King James Version, and not the other way around.[144]
| Priestly Source | Jahwist Source | KJV Genesis 2:4 | Abraham 5:4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| "These are the generations of the heavens and of the earth when they were created. | "In the day that the LORD God made the earth and the heavens." | "These are the generations of the heavens and of the earth when they were created, in the day that the LORD God made the earth and the heavens." | "And the Gods came down and formed these the generations of the heavens and of the earth, when they were formed in the day that the Gods formed the earth and the heavens." |
Hebrew studies
[edit]

In early 1836 Joseph Smith and other leading Latter Day Saints paid Hebrew teacher Joshua Seixas to teach Hebrew. Seixas had created materials with a distinctive Sephardic transliteration system that was different than what was being taught elsewhere. Most distinct were the pronunciations for vowels and gutturals such as "au" used for qametz, "ee" for hireq, and "ng" for ayin.[171]
The creation story in the Book of Abraham and explanations of the facsimiles contain numerous Hebrew vocabulary words spelled using the unique transliteration system taught by Seixas.[161] Smith did not conceal that Hebrew was incorporated in the text of the Book of Abraham, rather he openly acknowledged it.[170][172] Smith, like many scholars and theologians of his day believed that Hebrew and Egyptian were related, and close to the pure language spoken by Adam in the Garden of Eden.[170]
| Word | Location | Book of Abraham explanation | Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gnolaum | Abraham 3:18 | "eternal" | Is Hebrew for "eternity" (נֵצַח). The spelling reflects Seixas' unique transliteration rules. An extant 1842 manuscript shows the word was initially "immortal" but was crossed out and replaced with "Gnolaum".[170][173] |
| Hah-ko-kau-beam | Facsimile #2 | name of a star | Is Hebrew for "the stars" (הכוכבים), with the article "the" and plural. The spelling reflects Seixas unique transliteration rules.[170] |
| Jah-oh-eh | Facsimile #2 | Egyptian for "measurement of the earth" | A 19th century criticism was that the word resembled the Hebrew word יהוה [Jehovah].[74] Modern scholars find this unlikely and a weak connection to Hebrew.[170] |
| Kokaubeam | Abraham 3:13 | "stars, or all the great lights" | Is Hebrew for "stars" (כוכבים), without the article "the" and plural. The spelling reflects Seixas unique transliteration rules.[170] |
| Kokob | Abraham 3:13 | "star" | Is Hebrew for "star" (כוכב), without the article "the" and singular. The spelling is standard, and appears in the Gesenius lexicon.[170] |
| Kolob | Facsimile #2, Abraham 3:2–16 | "nearest unto the throne of God" | Some scholars have suggested that the Hebrew verb קָרֵב (QRB) "to draw near" is a form of KLB[Kolob].[174] |
| Libnah | Facsimile #1, Abraham 1:6-17 | Name of Egyptian God | Several scholars have suggested that Smith could have obtained this from the words Laban לָבָן (white) or l'banah לְבָנָה (moon).[175] Matthew Grey disagrees, pointing out that in the earliest Book of Abraham manuscripts, the word was originally translated as Zibnah[170][176] |
| Raukeeyang, Shaumau and Shaumahyeem | Facsimile #1 | In reference to the hatched lines (Nile river) "Raukeeyang, signifying expanse, or the firmament over our heads; but in this case, in relation to this subject, the Egyptians meant it to signify Shaumau, to be high, or the heavens, answering to the Hebrew word, Shaumahyeem."
The bottom decoration of the facsimile is described as being "Designed to represent the pillars of heaven, as understood by the Egyptians." |
Raukeeyang (רָקִיעַ) is interpreted firmament, but is translated as expanse in Seixas manuals, following a movement in the early 19th century to change the translation to be more scientific. The spelling of Raukeeyang utilizes the unique transliteration of Seixas.[170]
Shaumahyeem (שמים) is a plural word for heavens that also closely follows Seixas grammar.[170] The word Shaumau is unattested in either Egyptian or Hebrew, but does appear in a Hebrew lexicon Smith seems to have had access to.[171][i] In the lexicon it refers to Shaumau as being the singular form of Shaumauhyeem and found in Arab as "to be high". The entry additionally refers to heaven as resting on pillars, similar to the facsimile #1 description of the bottom decoration.[170][169] |
Hebrew influence on the creation account
[edit]The Book of Abraham chapters 4 and 5 retains about 75 percent of the wording from the King James translation of Genesis 1 and 2. The remaining 25 percent shows heavy influence from Smith's Hebrew studies under Seixas. For instance, Smith's choice to render רָקִיעַ (which is traditionally translated as "firmament") as "expanse" reflected an early 19th century movement (and one that Seixas endorsed) to use a more scientific term. Similarly, Smith rendered what was traditionally translated as "moved upon the face of the waters" to "brooding upon the faces of the water", which reflected Seixas and other contemporary commentators' preferred rendering of the word. Some changes were grammatical in nature, such as changing divided to caused it to be divided. The Hebrew וַיְהִ means "and it was" or "and it came to pass" and is left off in the King James Version of the Bible, but appears in Seixas translation and also throughout the Book of Abraham. During his time working with Seixas, Smith was using Joshua Seixas's A Manual Hebrew Grammar for the Use of Beginners (1834) as a textbook, and he may have also read Wilhelm Gesenius's A Hebrew and English Lexicon of the Old Testament (1824).[170]
Two Hebrew translations in the Book of Abraham had a theological impact. Normally translated as singular, in the Book of Abraham the word Elohim (אֱלֹהִים) is translated to be plural "the Gods". The -im (ים-) ending on many Hebrew words makes it plural similar to how an 's' at the end of some English nouns makes the word plural.[29] Smith explained his reasoning for the translation in an 1844 discourse, saying that he "once asked a learned Jew ... if the Hebrew language compels us to render all words ending in heam in the plural-why not render the first plural-he replied it would ruin the Bible-he acknowledged I was right."[170][j] Of note, Gesenius's lexicon does note that Elohim can be translated in the plural but that in Genesis 1:1 it is singular.[170][179]
The second theologically impactful translation was different than that suggested by Seixas, but followed the Gesenius lexicon. The words "create" and "to make" were translated as "to organize" and "to form" in keeping with Latter Day Saint theology against creation from nothing.[170]
1833 Patriarchal Blessing
[edit]An explanatory note written by Oliver Cowdery to a patriarchal blessing given by Smith to Cowdery has been suggested as a source for the wording in Abraham 1:2.[180] The note discusses the events that Cowdery said led to his being given the Melchizedek priesthood by angels. Richard Lloyd Anderson wrote that "the entry originated December 13, 1833", and was "the earliest known account of priesthood restoration."[181] In suggesting that the papyri was a catalyst, BYU Professor James Harris wrote, "The near identical wording of these passages would indicate that some of the text of the Book of Abraham was revealed and recorded before the Abraham papyri came into the possession of Joseph Smith."[180]
| Abraham 1:2 | Oliver Cowdery note |
|---|---|
| I sought for the blessings of the father, and the right where unto I should be ordained to administer the same; having been myself a follower of righteousness, desiring also to be one who possessed great knowledge, and to be a greater follower of righteousness and to possess a greater knowledge ... | ... we diligently sought for the right of the fathers, and the authority of the Holy Priesthood, and the power to administer in the same; for we desired to be followers of righteousness and the possessors of greater knowledge, even the knowledge of the mysteries of the Kingdom of God. |
Historian Dan Vogel has argued that the dependency is the other way around, that Cowdery was influenced by the Book of Abraham when writing his note. He points out that Cowdery was called as the primary scribe for patriarchal blessings around September 1835 and probably added the note when he copied the earlier blessing into the patriarchal blessing book.[182][183]
Thomas Dick's A Philosophy of a Future State
[edit]The Book of Abraham has a section on astronomy discussing the throne of God as being the center of the Universe, and "intelligences" (souls) that God created, who progressed eternally.[184] Several historians, including Fawn M. Brodie, have argued that these ideas came directly from Thomas Dick and his popular book A Philosophy of a Future State, which similarly discusses grades of "intelligences" created by God who eternally progress, and a system of astronomy with God's throne at the very center.[185] Sidney Rigdon quoted from Dick's book in 1836, Oliver Cowdery published a passage of the book in the Messenger and Advocate, and in January 1844 Smith himself donated his copy of Dick's book to the Nauvoo library in 1844.[186][187] That said, the historian John L. Brooke notes that there are several other contemporary sources besides Dick that could have been the source of inspiration for the Book of Abraham.[186] LDS historian Benjamin Park similarly notes that the direct link to Dick is tenuous and the ideas could have come from the cultural milieu.[187]
Pure language project
[edit]Throughout Joseph Smith's ministry he had an interest in the language spoken by Adam in the Garden of Eden, which he considered "pure and undefiled".[188] Smith believed that Egyptian and Hebrew were closely related to the pure language.[170] In 1832 Smith received a revelation restoring various Adamic words.[189] In May 1835, a few months before purchasing the papyri, Smith's scribe W.W. Phelps wrote a letter to his wife detailing a list of pure language terms, which were also included in an Egyptian alphabet document a few months later.[190][191]
The Book of Abraham includes two terms that are neither Egyptian nor Hebrew, shinehah and olea translated as "sun" and "moon" respectively.[192][k] Both terms appear in an 1838 revelation[194] in the context of another pure language word Adam-ondi-ahman, indicating that they are also pure language terms.[188]
-
Sample of Pure Language, in a letter from William W. Phelps to his wife Sally on May 26, 1835, written one month prior to the arrival of the Papyri to Kirtland[190]
-
Section of Egyptian Alphabet in Joseph Smith's handwriting, with pure language characters and Egyptian translation[195]
Ethics
[edit]Black people and the curse of Ham
[edit]In the Book of Abraham, Pharaoh and his lineage are denied the priesthood because they are descendants of Ham through Canaan who was cursed.[196] The belief that black people were descendants of Ham was a popular antebellum belief, and early Latter Day Saints were predisposed to read the text in this context.[197] In April 1836, within months of translating these verses, Joseph Smith himself taught in reference to Genesis 9:25–27, "it remains as a lasting monument of the decree of Jehovah, to the shame and confusion of all who have cried out against the South, in consequence of their holding the sons of Ham in servitude!"[198][199] When combined with verses from the Book of Moses which associated the curse of Canaan with blackness, the Book of Abraham was used by LDS leaders as early as 1845 to justify anti-black practices in the LDS Church, such as priesthood denial and policies against interracial marriage.[200]
In 2013 the LDS Church released a statement, "Black servitude was sometimes viewed as a second curse placed upon Noah's grandson Canaan as a result of Ham's indiscretion toward his father. ... Today, the Church disavows the theories advanced in the past that black skin is a sign of divine disfavor or curse."[200] The modern position by the LDS Church is that the passage has been misinterpreted, and it is more about priesthood lineage determined by birth order, not racial lineage.[197][199]
Use of pagan symbols
[edit]A religious criticism by Charles M. Larson is that because God rebuked and punished the Israelites anytime they lapsed into paganism or mingled with the followers of other deities, and because the New Testament claims that "God does not use pagan or ungodly vessels to bear his Truth," the claim that the Book of Abraham was found in Egyptian (that is, pagan) religious documents conflicts directly with what is written in the Bible.[201]
Defense of the book
[edit]A number of theories have been presented in defense of the official LDS Church position that the work is a revelation from God, through Joseph Smith, which tells a true story of actual events from the life of Abraham. The most common of these arguments is that Smith interpreted the documents by revelation, rather than a standard "translation" of text from one language to another, in a process similar to his translation of the Bible.[59][202] In 2014, the LDS Church published an essay on its website which acknowledged that Joseph Smith's notes concerning the meaning of the Egyptian characters are inconsistent with "those recognized by Egyptologists today" and that "Mormon and non-Mormon Egyptologists agree that the characters on the fragments do not match the translation given in the book of Abraham."[130] However, the essay points out that it was not uncommon for ancient Egyptian vignettes to be placed some distance from their associated commentary, thus text adjacent to and surrounding facsimile 1 may not be a source for the text of the Book of Abraham.[130][203] The essay concluded that "the truth of the Book of Abraham is ultimately found through careful study of its teachings, sincere prayer, and the confirmation of the Spirit" and "cannot be settled by scholarly debate concerning the book's translation and historicity."[130]
Other apologetic arguments do not deny the meaning of the papyri as determined by Egyptologists, but in addition propose that the hieroglyphic text has some hidden meaning. Some apologists argue that there are other messages and meanings embedded in the text along with the Egyptologist's translations that are unknown to us.[l] For many years, Hugh Nibley, for instance, preferred the argument that the Sensen text has two meanings: one that can be determined by standard translation (a "literal translation"), and another (a "secret meaning") that can only be divined, possibly with the help of a tool like the Urim and Thummim or one of the seer stones that Joseph Smith purportedly used to translate the Book of Mormon.[205] Similarly, Richley Crapo and John Tvedtnes proposed that the Sensen text may have merely been a mnemonic device, used "to bring to mind 'a set number of memorized phrases relating to Abraham's account of his life.'"[206][207][208][209][210][211] Crapo and Tvedtnes argued that, were one to compare the literal meaning of the hieroglyphic characters found in the Sensen text with the Book of Abraham, certain parallels could be found; for instance, the first hieroglyph found in the Sensen text means "this", and Crapo and Tvedtnes pointed out that the opening of Abraham 1:11 reads, "Now this priest had offered ..."[211] This argument was popular within LDS circles, but Klaus Baer criticized it because the supposed parallels offered were "related by no visible principle" and instead seemed to have been made ad hoc.[211]
In regards to the connection between the Sensen text and the Kirtland Egyptian Papers, some argue that a relationship exists only because the latter is a product of Smith's scribes (as opposed to Smith himself), who, out of personal curiosity, were trying to reverse-engineer the meaning of the Egyptian hieroglyphs. In other words, this hypothesis posits that the scribes wrote down the characters from the Sensen text and then, via speculation, attempted to match the characters with what had been revealed to Smith. However, Smith's own diary entries (as collected in the History of the Church) record that in July 1835, he was "continually engaged in translating an alphabet to the Book of Abraham", which suggests Smith was actively involved in the creation of the Kirtland Egyptian Papers, thus weakening this apologetic hypothesis.[212]
It has also been argued that the methodology used by modern Egyptologists to translate ancient records is unreliable and unstable, and therefore produces flawed and nonsensical translations. Thus, the modern translations of the Joseph Smith Papyri as produced by Egyptologists are not to be trusted. This line of thinking was used by Nibley in his 1975 book, The Message of the Joseph Smith Papyri. He wrote: "To the often asked question, 'Have the Joseph Smith Papyri been translated?' The answer is an emphatic no! What, then, is the foregoing? A mechanical transcription, no more ... What we have is a transmission rather than a translation of the text ... Though as correct and literal as we can make it, the translation in the preceding chapter is not a translation. It is nonsense."[213]
Finally, it has been proposed that the remaining papyrus fragments are only part of the complete original papyri.[70] Contemporary accounts refer to "a long roll" or multiple "rolls" of papyrus.[130] In 1968, Keith C. Terry and Walter Whipple estimated that the fragments constituted roughly one-third of Smith's original collection of papyri.[214] Later, in 2000, Mormon Egyptologist John Gee provided a graphical comparison of the relative extent of the known fragments to other complete examples of similar scrolls, which indicated the total at about twenty percent.[215] Others, however, have challenged this notion, contending that the majority of the papyri have been recovered. Andrew Cook and Christopher Smith, for example, argue that, based on a physical analysis of fragments from the scroll of Hôr, only 56 cm (22 in) could be missing from that scroll. This contrasts with an LDS scholar's earlier estimate for the length of the missing portion.[216][217] Still others have suggested that fragments may have only been a starting point for reconstruction.[218][219]
See also
[edit]- Mormon cosmology
- Criticism of the Latter Day Saint movement
- Criticism of Mormon sacred texts
- Kirtland Egyptian Papers
Notes
[edit]- ^ Facsimile No. 1 and Chapter 1 through chapter 2 verse 18 are to be found in Volume III, No. 9, dated March 1, 1842; Facsimile No. 2 and chapter 2 verses 19 through chapter 5 are to be found in Volume III, No. 10, dated March 15, 1842; Facsimile No. 3 are to be found in Vol. III, No. 14, dated May 16, 1842.[32]
- ^ Stephen Thompson notes that at least "four anachronistic names [are found] in the text: Chaldea, Potiphar, Egyptus, and probably Pharaoh".[60]
- ^ Whoever created the correlation often failed to properly determine where the Egyptian characters began or ended, as many of the transliterated characters found in the "Egyptian Alphabet and Grammar" are either improperly split or inappropriately combined with elements of other characters.[68]
- ^ Including: A. H. Sayce of Oxford University, W. M. Flinders Petrie of London University, James H. Breasted of the University of Chicago Haskell Oriental Museum, Arthur C. Mace of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York, John Punnett Peters of the University of Pennsylvania, C. A. B. Mercer of the Western Theological Seminary, Edward Meyer of the University of Berlin, and Friedrich Freiheer von Bissing of the University of Munich.[76]
- ^ The name "Hôr" is rendered in some sources as "Horus".[90]
- ^ Apologist Michael R. Ash has noted: "The late Klaus Baer, a non-LDS Egyptologist from the University of Chicago, claimed the Facsimile 1 and 3 are unusual and it would be erroneous to claim that dozens of similar examples could be found. 'Facsimile 3,' he went on to note, 'is not a judgment scene [as often claimed by critics] and exact parallels may be hard to find.'"[123]
- ^ Rhodes says that "Baer's, Coenen and Quackenbur's assumption that the missing portion would show an erect phallus with a hawk above it representing the conception of Osiris is not likely since the figure on the couch is wearing a kilt. Also the position of the hand of Anubis would be where the erect phallus would be. In all representations showing Osiris with an erect phallus, he is nude."[125]
- ^ In Praeparatio evangelica 9.17.2–9, Eusebius quotes Pseudo-Eupolemus, and the text reads: "And Abraham dwelt with the Egyptian priests in Heliopolis and taught them many things; and it was he who introduced astronomy and the other sciences to them, saying that the Babylonians and himself had found these things out, but tracing back the first discovery to Enoch, and saying that he, and not the Egyptians, had first invented astrology."[132]
- ^ a b A document titled "List of works in Hebrew Greek Latin Syraic Arabic Chaldaee & English" is a circa 1836 document listing over forty lexicons, grammars, and textbooks that the Kirtland school had either purchased or desired. This list included an edition of the Gesenius lexicon translated by Gibbs.[177]
- ^ Smith may also have been encouraged in the idea by several other Bible commentaries available at the time that argued that the plurality of the word could refer to the Trinity or multiple Gods.[178]
- ^ The word shinehah was included in the 1835 version of the Doctrine and Covenants as a code for Kirtland.[193]
- ^ Michael D. Rhodes admits that "we can, with the help of other similar texts, reconstruct the text and figures of the Joseph Smith Hypocephalus with a fair degree of accuracy," but believes that, "we are still far from completely understanding the message which the Egyptians meant to convey by it. The text of the hypocephalus itself seems to be an address to Osiris, the god of the Dead, on behalf of the deceased, Sheshonk. As is the case with most Egyptian texts (especially religious text), it is full of references to matters either obscure or unknown to us, although undoubtedly clear to the Egyptians. Needless to say, much work is still to be done before we can fully understand the import of the Joseph Smith Hypocephalus, and hypocephali in general."[204]
References
[edit]Footnotes
[edit]- ^ a b c Smith (1842), p. 704.
- ^ a b c d Ritner, Robert K., A Response to 'Translation and Historicity of the Book of Abraham', Signature Books, archived from the original on April 4, 2017
- ^ a b Gee (2000a), pp. 4–6.
- ^ "The Book of Abraham". The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 55.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 61.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 306.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 326.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 310.
- ^ Chase (2014), p. 160.
- ^ Abraham 1:1–4.
- ^ Abraham 3.
- ^ Abraham 2:10.
- ^ Abraham 3:18–28.
- ^ Abraham 4:1.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), pp. 14–15.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 1.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 15.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 2.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 15–17.
- ^ Vogel (2021), p. 19.
- ^ Smith (1948), p. 238.
- ^ Jessee (2002), p. 86.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 18.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), pp. 19–21.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 20.
- ^ a b c Ritner (2013), p. 21.
- ^ a b c d Smith (1990), p. 169.
- ^ a b Givens & Hauglid (2019), p. 140.
- ^ Ritner (2013), pp. 19, 23–24, 31–32.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 27.
- ^ Smith (1842).
- ^ Peterson (1995), p. 16.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 64.
- ^ Wade et al. (1967), p. 64.
- ^ a b Barney (2006).
- ^ Vogel (2021), pp. 64–65.
- ^ Ritner (2013), pp. 65–66.
- ^ Deseret News, Salt Lake City, November 27, 1967.
- ^ Larson (1992), p. 54.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 66.
- ^ G (1968), p. 40.
- ^ Todd (1968), pp. 39–46.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968), pp. 67–99.
- ^ Baer (1968), pp. 109–54.
- ^ Ritner (2000), p. 97.
- ^ a b Rhodes (2005).
- ^ Gee (1999).
- ^ a b Ritner (2003).
- ^ Larson (1992), p. 61.
- ^ a b Reeve & Parshall (2010), p. 269.
- ^ a b Ashment (2000), p. 126.
- ^ Rhodes (2005), p. 1.
- ^ Baer (1968), pp. 116–17.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968), p. 98.
- ^ a b Baer (1968), p. 111.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968), pp. 95–96.
- ^ Nibley (1975), p. 3.
- ^ a b Rhodes (1988), pp. 51–53.
- ^ Thompson (1995), pp. 152–56.
- ^ The source of Joseph Smith's quotes cited here are found in Smith (1842), p. 704 and Smith (1990), p. 169, respectively.
- ^ For fragments: I–XI, see: Ritner (2013), p. 65. For the sources of Facsimile No. 2 and 3, see: Ritner (2013), p. 66.
- ^ For fragments: I–XI, see: Ritner (2013), p. 65. For the source of Facsimile No. 2, see: Ritner (2013), pp. 66, 263. For the source of Facsimile No. 3, see: Ritner (2013), p. 66.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 65.
- ^ Ritner (2013), pp. 61–66.
- ^ a b c Larson (1992), p. 66.
- ^ Ashment (2000), pp. 121–22.
- ^ Larson (1992), pp. 96–97.
- ^ a b Wilson et al. (1968), p. 95.
- ^ a b Larson (1992), pp. 129–34.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 62.
- ^ a b c Larson (1992), p. 25.
- ^ Larson (1992), p. 26.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Deveria as quoted in Stenhouse (1873), pp. 510–19.
- ^ Larson (1992), p. 27.
- ^ Spaulding (1912), pp. 23–31.
- ^ Spaulding (1912).
- ^ Spaulding (1912), pp. 26–27.
- ^ Spaulding (1912), p. 24.
- ^ Spaulding (1912), p. 23.
- ^ Larson (1992), p. 29.
- ^ Webb (1915), pp. 30–31.
- ^ Abraham 1:12.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 58.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968), p. 68.
- ^ Baer (1968), p. 118.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968), p. 86.
- ^ Deveria as quoted in Stenhouse (1873), pp. 513–14.
- ^ Ritner (2013), pp. 101–86.
- ^ E.g. Marquardt (2017).
- ^ "Facsimile No. 1". The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ Ritner (2013), pp. 117–18.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 117.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 113.
- ^ a b c d Ritner (2013), pp. 113–14.
- ^ a b c d Ritner (2013), p. 114.
- ^ Pinch (1995), p. 157.
- ^ Ritner (2003), p. 263.
- ^ "Facsimile No. 2". The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 271.
- ^ a b c d e Gee (1991).
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 268.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 270.
- ^ Ritner (2013), pp. 273–74.
- ^ a b Ritner (2013), p. 274.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 272.
- ^ a b c d Parker as quoted in Larson (1992), p. 107.
- ^ a b Rhodes as quoted in Larson (1992), p. 107.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 275.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 267.
- ^ a b c Rhodes, Michael D. (1996), The Joseph Smith Hypocephalus: Seventeen Years Later, Light Planet, archived from the original on August 22, 2017
- ^ Thompson (1995), p. 145.
- ^ a b c Thompson (1995), p. 144.
- ^ "Facsimile No. 3". The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f Ritner (2003), pp. 176–77.
- ^ Larson (1992), p. 155.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968).
- ^ Baer (1968).
- ^ Ritner (2000).
- ^ a b Larson (1992), pp. 104–08.
- ^ Wilson et al. (1968), pp. 96–98.
- ^ Gee (2000b), pp. 175–217.
- ^ Gee (1992), p. 100.
- ^ Rhodes (2003).
- ^ Rhodes (2005), p. 19.
- ^ Nibley (1980), pp. 89–90.
- ^ Nibley (1980), pp. 90–91.
- ^ Tvedtnes et al. (2001), p. 540.
- ^ a b Gee (2011), pp. 137–56.
- ^ a b c d e f "Translation and Historicity of the Book of Abraham". The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ Tvedtnes et al. (2001), p. 545.
- ^ Eusebius, Praeparatio evangelica 9.17.2–9.
- ^ Tvedtnes et al. (2001), p. 544.
- ^ Moore & Kelle (2011), pp. 18–19.
- ^ a b Thompson (1995), p. 154
- ^ Muhlestein (2006).
- ^ Barney (2006), pp. 115–16.
- ^ Rhodes (2003), pp. 115–23.
- ^ Peterson (1995), p. 27.
- ^ a b Harris et al. (2020). e-book location 6445 of 8366.
- ^ Coogan (2009).
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 117
- ^ Viviano (1999), pp. 38–39.
- ^ a b c d Bokovoy (2014), p. 165.
- ^ Abraham 1:23–25.
- ^ a b Thompson (1995), p. 155
- ^ Mekis (2020), p. 2.
- ^ Cooper (1987), p. 63.
- ^ Skousen (2019), p. 39.
- ^ Abraham 1:8–12
- ^ Abraham 1:9.
- ^ a b Ritner (2000), pp. 97–119.
- ^ Muhlestein (2008), pp. 181–208.
- ^ Gee & Muhlestein (2011).
- ^ Ritner (2003), pp. 161–180.
- ^ a b Abraham 1:20.
- ^ Thompson (1995), pp. 154–155.
- ^ Abraham 1:10.
- ^ Ritner (2013), p. 3
- ^ a b c Ritner (2013), p. 90.
- ^ a b Walton (1981).
- ^ Hutchinson (1988), pp. 11–74.
- ^ Sandberg (1989), pp. 17–38.
- ^ Sarna (1966), p. 98.
- ^ Excerpts from P. Leiden I 384 (PGM XII), in Tvedtnes et al. (2001), pp. 501–2, 523.
- ^ Betz (1986), p. 171.
- ^ Grey (2020), p. 433.
- ^ Seixas (1834), p. 78.
- ^ a b Gesenius (1824), p. 671.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Grey (2020), pp. 390–451.
- ^ a b Grey (2015), pp. 249–302.
- ^ Givens & Hauglid (2019), p. 115.
- ^ "Book of Abraham Manuscript, 8–circa 15 March 1842 [Abraham 3:18–26]". The Joseph Smith Papers. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- ^ Ogden (1990), p. 165.
- ^ Draper et al. (1990).
- ^ "Book of Abraham Manuscript, circa July–circa November 1835–C [Abraham 1:1–2:18], p. 1". The Joseph Smith Papers. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- ^ Grey (2020), p. 408, footnote 71.
- ^ Grey (2020), p. 439.
- ^ Gesenius (1824), p. 60.
- ^ a b Harris (1970), pp. 126–127.
- ^ Anderson (1968), p. 20 and footnote 16.
- ^ "Source note to 'Blessing from Joseph Smith Sr., 9 December 1834'". The Joseph Smith Papers. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ Vogel, Dan (September 6, 2018). "Truth of the Book of Abraham (Part 4) - Egyptian Grammar & Race". YouTube. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ Abraham 3.
- ^ Brodie (1971), pp. 171–172.
- ^ a b Brooke (1994), pp. 205–207.
- ^ a b Park (2012), pp. 210–224.
- ^ a b Golding (2020), p. 353.
- ^ "Sample of Pure Language, between circa 4 and circa 20 March 1832," p. 144". The Joseph Smith Papers. Retrieved May 23, 2020.
- ^ a b Hauglid (2015), pp. 474–511.
- ^ Jensen & Hauglid (2018), p. 54.
- ^ Abraham 3:13.
- ^ Whittaker (1983), p. 111.
- ^ Doctrine and Covenants 117:8: "Is there not room enough on the mountains of Adam-ondi-Ahman, and on the plains of Olaha Shinehah."
- ^ "Egyptian Alphabet, circa Early July–circa November 1835–A, Page 1". The Joseph Smith Papers. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ Abraham 1:21–27.
- ^ a b Givens & Hauglid (2019), p. 135.
- ^ "Letter to Oliver Cowdery, circa 9 April 1836". The Joseph Smith Papers. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ a b Bushman & Woodworth (2007). e-book location 6371 of 17510.
- ^ a b Harris et al. (2020).
- ^ Larson (1992), pp. 119–20.
- ^ Rhodes, Michael; Gee, John (January 29, 2006). "Interview on KSL Radio on January 29, 2006". KSL (Interview). Salt Lake City.
- ^ Davidson, Lee (July 8, 2014). "Mormon Essay: Abraham Scripture May Not Be Literal Translation". The Salt Lake Tribune. Archived from the original on August 24, 2017. Retrieved July 14, 2014.
- ^ Rhodes (1977).
- ^ Larson (1992), pp. 115–16.
- ^ Crapo & Tvedtnes (1968).
- ^ Crapo & Tvedtnes (1969a).
- ^ Crapo & Tvedtnes (1969b).
- ^ Crapo & Tvedtnes (1969c).
- ^ Tvedtnes (1970).
- ^ a b c Larson (1992), pp. 117–19.
- ^ Larson (1992), pp. 121–29.
- ^ Rhodes (1992), pp. 138–40.
- ^ Terry & Whipple (1968), p. 116.
- ^ Gee (2000a), pp. 12–13.
- ^ Cook & Smith (2010).
- ^ Smith (2011).
- ^ Gee (1992), pp. 93–119.
- ^ Rhodes (1992), pp. 120–26.
Bibliography
[edit]- Anderson, Richard Lloyd (September 1968). "The Second Witness of Priesthood Restoration". The Improvement Era. Retrieved January 11, 2023 – via The Internet Archive.
- Ashment, Edward H. (December 2000). "Joseph Smith's Identification of "Abraham" in Papyrus JS1, the "Breathing Permit of Hor"" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 33 (4): 121–6. doi:10.2307/45226744. JSTOR 45226744. S2CID 254298749. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 19, 2011.
- Baer, Klaus (November 1968). "The Breathing Permit of Hor: A Translation of the Apparent Source of the Book of Abraham" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 3 (3): 109–54. doi:10.2307/45224026. JSTOR 45224026. S2CID 254387471. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 19, 2011.
- Barney, Kevin (2006). "The Facsimiles and Semitic Adaptation of Existing Sources". In Gee, John; Hauglid, Brian M (eds.). Astronomy, Papyrus, and Covenant. Provo, UT: Brigham Young University. ISBN 9780934893763.
- Betz, Hans Dieter (1986). The Greek Magical Papyri In Translation. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Bokovoy, D. E. (2014). Authoring the Old Testament: Genesis-Deuteronomy. Salt Lake City, UT: Greg Kofford Books.
- Brodie, Fawn (1971). No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith. Brookfield, MA: E. and G. Merriam.
- Brooke, John L. (1994). The Refiner's Fire: The Making of Mormon Cosmology, 1644-1844. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Bushman, R. L.; Woodworth, J (2007). Joseph Smith: Rough Stone Rolling. New York City, NY: Vintage Books.
- Chase, Randal S. (2014). Pearl of Great Price Study Guide. Washington, UT: Plain & Precious Publishing. ISBN 9781937901134.
- Coogan, Michael D. (2009). A Brief Introduction to the Old Testament. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Cook, Andrew W.; Smith, Christopher C. (2010). "The Original Length of the Scroll of Hôr" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 43 (4): 1–42. doi:10.5406/dialjmormthou.43.4.0001. S2CID 171454962. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 11, 2016.
- Cooper, J. C. (1987). An Illustrated Encyclopaedia of Traditional Symbols. London, UK: Thames and Hudson.
- Crapo, Richley; Tvedtnes, John A. (October 1968). "A Study of the Hor Sensen Papyrus". Newsletter & Proceedings of the Society for Early Historic Archaeology (109).
- Crapo, Richley; Tvedtnes, John A. (March 1969a). "Rediscovery of Smith Papyri Affects Book of Abraham". LDS Student Association Commentary.
- Crapo, Richley; Tvedtnes, John A. (May 1969b). "Papyri Give Further Book of Abraham Insight". LDS Student Association Commentary.
- Crapo, Richley; Tvedtnes, John A. (June 1969c). "The Hor Sensen Papyrus as a Mnemonic Device: A Further Study". Newsletter & Proceedings of the Society for Early Historic Archaeology (114).
- Draper, R. D.; Brown, S. K.; Rhodes, M. D. (2005). The Pearl of Great Price: A Verse-by-Verse Commentary. Salt Lake City, UT: Deseret Book.
- Duis, Perry (1998). Challenging Chicago: Coping with Everyday Life, 1837–1920. Champaign, IL: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 9780252023941.
- G, D. L. (February 1968). "New Light on Joseph Smith's Egyptian Papyri: Additional Fragment Disclosed". Improvement Era. Vol. 71, no. 2. p. 40. Retrieved August 9, 2016 – via The Internet Archive.
- Gee, John (1991). Notes on the Sons of Horus. Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies. Retrieved January 11, 2023.
{{cite book}}:|newspaper=ignored (help) - Gee, John (1992). "A Tragedy of Errors". Mormon Studies Review. 4 (1): 93–. doi:10.2307/44796510. JSTOR 44796510. Archived from the original on August 24, 2017.
- Gee, John (1999). The Ancient Owners of the Joseph Smith Papyri. Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies. Retrieved January 11, 2023.
{{cite book}}:|newspaper=ignored (help) - Gee, John (2000a). A Guide to the Joseph Smith Papyri. Provo, UT: Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies. ISBN 9780934893541.
- Gee, John (2000b). "Eyewitness, Hearsay, and Physical Evidence of the Joseph Smith Papyri". In Ricks, Steven; Parry, Donald; Hedges, Andrew (eds.). The Disciple as Witness: Essays on Latter-day History and Doctrine. Provo, UT: Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies. ISBN 9780934893459.
- Gee, John (2011). "An Egyptian View of Abraham". In Skinner, Andrew C; Davis, Morgan; Griffin, Carl (eds.). Bountiful Harvest: Essays in Honor of S. Kent Brown. Provo, UT: Neal A. Maxwell Institute for Religious Scholarship. pp. 137–56. ISBN 9780842528047.
- Gee, John; Muhlestein, Kerry (2011). "An Egyptian Context for the Sacrifice of Abraham". Journal of Book of Mormon Studies. 20 (2). Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- Gesenius, Wilhelm (1824). A Hebrew and English Lexicon of the Old Testament, Including the Biblical Chaldee. Translated by Josiah W. Gibbs. Andover, MA: Flagg and Gould. Retrieved January 11, 2023 – via Google Books.
- Givens, T.; Hauglid, B. M. (2019). The Pearl of Greatest Price: Mormonism's Most Controversial Scripture. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Golding, David (2020). "Eternal Wisdom Engraven upon the Heavens:Joseph Smith's Pure Language Project". In MacKay, M. H.; Ashurst-McGee, M.; Hauglid, B. M. (eds.). Producing Ancient Scripture: Joseph Smith's Translation Projects in the Development of Mormon Christianity. Salt Lake City, UT: The University of Utah Press.
- Grey, Matthew J. (2015). "'The Word of the Lord in the Original': Joseph Smith's Study of Hebrew in Kirtland". In Lincoln H. Blumell; Matthew J. Grey; Andrew H. Hedges (eds.). Approaching Antiquity: Joseph Smith and the Ancient World. Provo, UT: Religious Studies Center.
- Grey, Matthew J. (2020). "Approaching Egyptian Papyri through Biblical Language: Joseph Smith's Use of Hebrew in His Translation of the Book of Abraham". In MacKay, M. H.; Ashurst-McGee, M.; Hauglid, B. M. (eds.). Producing Ancient Scripture: Joseph Smith's Translation Projects in the Development of Mormon Christianity. Salt Lake City, UT: The University of Utah Press.
- Harris, James R. (1970). "Review of 'The Saga of the Book of Abraham by Jay M. Todd". BYU Studies Quarterly. 10 (1): 125–27. Retrieved January 11, 2023.
- Harris, M. L.; Bringhurst, N. G.; Mauss, A. L. (2020). The LDS Gospel Topics Series: A Scholarly Engagement. Salt Lake City, UT: Signature Books.
- Hauglid, Brian M. (2015). "The Book of Abraham and the Egyptian Project: 'A Knowledge of Hidden Languages'". In Lincoln H. Blumell; Matthew J. Grey; Andrew H. Hedges (eds.). Approaching Antiquity: Joseph Smith and the Ancient World. Provo, UT: Religious Studies Center.
- Hutchinson, Anthony (1988). "A Mormon Midrash? LDS Creation Narratives Reconsidered". Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 21 (4): 11–74. doi:10.2307/45225679. JSTOR 45225679.
- Jensen, Robin Scott; Hauglid, Brian M., eds. (2018). Revelations and Translations, Volume 4: Book of Abraham and Related Manuscripts. Facsimile edition. Revelations and Translations series of The Joseph Smith Papers. Salt Lake City, UT: Church Historian’s Press.
- Jessee, Dean (2002). Personal Writings of Joseph Smith. Salt Lake City, UT: Deseret Book. ISBN 9781573457873.
- Larson, Charles M. (1992). By His Own Hand Upon Papyrus (2 ed.). Cedar Springs, MI: Institute of Religious Research. ISBN 9780962096327.
- Marquardt, H. Michael (August 1, 2017). "Breathing Permit of Horus". XMission. Archived from the original on August 24, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Mekis, Tamás (2020). The Hypocephalus: An Ancient Egyptian Funerary Amulet. Oxford, UK: Archaeopress.
- Moore, Megan Bishop; Kelle, Brad E. (2011). Biblical History and Israel's Past. Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans. ISBN 978-0-8028-6260-0.
- Muhlestein, Kerry (2006). "Approaching Understandings in the Book of Abraham". Review of Books on the Book of Mormon. 18 (2). Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- Muhlestein, Kerry (2008). "Royal Executions: Evidence Bearing on the Subject of Sanctioned Killing in the Middle Kingdom". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 51 (2): 181–208. doi:10.1163/156852008X307429.
- Nibley, Hugh (1975). The Message of the Joseph Smith Papyri: An Egyptian Endowment. Salt Lake City, UT: Deseret Book. ISBN 9781590385395.
- Nibley, Hugh (1980). The Three Facsimiles from the Book of Abraham (PDF). Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 24, 2017.
- Ogden, D. Kelly (1990). "The Kirtland Hebrew School (1835-36)". In Milton V. Backman Jr. (ed.). Regional Studies in Latter-day Saint Church History. Provo, UT: Brigham Young University.
- Park, Benjamin E. (2012). "'Reasonings Sufficient': Joseph Smith, Thomas Dick, and the Context(s) of Early Mormonism". Journal of Mormon History. 38 (3): 210–224. doi:10.2307/23291624. JSTOR 23291624. S2CID 254485920.
- Peterson, H. Donl (1995). Story of the Book of Abraham: Mummies, Manuscripts, and Mormonism. Salt Lake City, UT: Deseret Book. ISBN 9780875798462.
- Pinch, Geraldine (1995). Magic in Ancient Egypt. Austin, Texas: University of Texas Press. ISBN 9780292765597.
- Reeve, W. Paul; Parshall, Ardis, eds. (2010). "Mormon Scripture". Mormonism: A Historical Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 9781598841084.
- Rhodes, Michael (Spring 1977). "Translation of Fac. #2". BYU Studies Quarterly (3). Archived from the original on July 7, 2012. Retrieved August 20, 2016.
- Rhodes, Michael (1988). "I Have a Question". Ensign. pp. 51–3. Retrieved August 20, 2016.
- Rhodes, Michael (1992). "The Book of Abraham: Divinely Inspired Scripture" (PDF). FARMS Review of Books. 4 (1). Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies: 120–6. doi:10.2307/44796511. JSTOR 44796511. S2CID 55005625. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 12, 2017.
- Rhodes, Michael (2003). "Teaching the Book of Abraham Facsimiles". The Religious Educator. 4 (2): 115–23.
- Rhodes, Michael (2005). The Hor Book of Breathings: A Translation and Commentary. Provo, UT: Brigham Young University. ISBN 9780934893633.
- Ritner, Robert K. (December 2000). "The "Breathing Permit of Hor" Thirty Four Years Later" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 33 (4): 97–119. doi:10.2307/45226742. JSTOR 45226742. S2CID 254348028. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 19, 2011.
- Ritner, Robert K. (July 2003). "'The Breathing Permit of Hôr' Among the Joseph Smith Papyri". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 62 (3): 161–180. doi:10.1086/380315. S2CID 162323232.
- Ritner, Robert K. (2013). The Joseph Smith Egyptian Papyri: A Complete Edition. Salt Lake City, UT: Signature Books. ISBN 9781560852209.
- Sandberg, Karl C. (1989). "Knowing Brother Joseph Again: The Book of Abraham and Joseph Smith as a Translator". Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 22 (4): 17–37. doi:10.2307/45228258. JSTOR 45228258. S2CID 254389117.
- Sarna, N. (1966). Understanding Genesis. New York City, NY: Schocken Books.
- Seixas, Joshua (1834). A Manual Hebrew Grammar for the Use of Beginners. Andover, MA: Gould and Newman.
- Skousen, Royal (2019). "Royal Skousen Fundamental Scholarly Discoveries and Academic Accomplishments" (PDF). humanities.byu.edu/. Brigham Young University. Retrieved July 26, 2020.
- Smith, Christopher C. (Spring–Summer 2011). ""That Which Is Lost": Assessing the State of Preservation of the Joseph Smith Papyri". John Whitmer Historical Association Journal. 31 (1): 69–83.
- Smith, Joseph (March 1, 1842). "Truth Will Prevail". Times and Seasons. Vol. 3, no. 9. Nauvoo, IL. p. 704. Archived from the original on May 30, 2012. Retrieved August 20, 2016.
- Smith, Joseph (1948). History of the Church of Jesus Christ of the Latter-Day Saints. Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). Salt Lake City, UT: Deseret News. Retrieved January 11, 2023 – via The Internet Archive.
- Smith, Milan D. Jr (December 1990). "That is the Handwriting of Abraham" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 23 (4): 167–9. doi:10.2307/45225946. JSTOR 45225946. S2CID 254312026. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 20, 2011.
- Spaulding, F. S. (1912). Joseph Smith, Jr. As a Translator: An Inquiry. Salt Lake City, UT: The Arrow Press. Retrieved August 3, 2016 – via The Internet Archive.
- Stenhouse, T. B. H. (1873). The Rocky Mountain Saints. New York City, NY: D. Appleton and Company – via The Internet Archive.
- Terry, Keith; Whipple, Walter (1968). From the Dust of Decades: Saga of the Papyri and Mummies. Salt Lake City, UT: Bookcraft.
- Thompson, Stephen E. (May 1995). "Egyptology and the Book of Abraham" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 28 (1): 143–60. doi:10.2307/45228487. JSTOR 45228487. S2CID 254346225. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 19, 2011.
- Todd, Jay M. (1968). "Background of the Church Historian Fragment". Improvement Era. Vol. 71, no. 2. pp. 39–49. Retrieved August 9, 2016 – via The Internet Archive.
- Todd, Jay M. (1992). "Papyri, Joseph Smith". In Ludlow, Daniel (ed.). Encyclopedia of Mormonism. London, UK: Macmillan Publishers.
- Tvedtnes, John A. (April 1970). "The Use of Mnemonic Devices in Oral Traditions, as Exemplified by the Book of Abraham & the Sensen Papyrus". Newsletter & Proceedings of the Society for Early Historic Archaeology (120).
- Tvedtnes, John A.; Hauglid, Brian M; Gee, John, eds. (2001), Traditions about the Early Life of Abraham, Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies
- Viviano, Pauline A. (1999). "Source Criticism". In Haynes, Stephen R.; McKenzie, Steven L. (eds.). To Each Its Own Meaning: An Introduction to Biblical Criticisms and Their Application. London, UK: Westminster John Knox. pp. 38–39. ISBN 978-0-664-25784-2.
- Vogel, Dan (2021). Book of Abraham Apologetics: A Review and Critique. Signature Books. ISBN 978-1-56085-290-2.
- Wade, Glen; Tolk, Norman; Travers, Lynn; Smith, George D; Graves, F. Charles (Winter 1967). "The Facsimile Found" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 2 (4): 51–64. doi:10.2307/45223944. JSTOR 45223944. S2CID 254399116. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 19, 2011.
- Walton, Michael T. (1981). "Professor Seixas, the Hebrew Bible, and the Book of Abraham" (PDF). Sunstone. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- Webb, Robert C. (1915). The Case Against Mormonism. New York City, NY: L. L. Walton – via The Internet Archive.
- Whittaker, David J. (1983). "Substituted Names in the Published Revelations of Joseph Smith". BYU Studies Quarterly. 23 (1): 103–112. ISSN 2167-8472. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- Wilson, John A.; Parker, Richard A; Howard, Richard A; Hewerd, Grant S; Jerald, Tanner; Hugh, Nibley (August 1968). "The Joseph Smith Egyptian Papyri" (PDF). Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought. 3 (2): 67–105. doi:10.2307/45227259. JSTOR 45227259. S2CID 254343491. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 19, 2011.
External links
[edit]- Translation and Historicity of the Book of Abraham, from the LDS Church website
- Joseph Smith Papers Project Egyptian Material
- Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought, an independent Mormon journal with scholarly works on the Book of Abraham