Wokshop de Git
- 1. GIT workshop
- 2. usando Git desde 2008
- 3. O que é um SCM?
- 4. svn VS git
- 5. SVN it svn m u om pd svnc ate
- 6. GIT git ush pu gi tp ll git push remote git pull remote
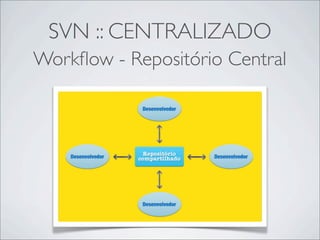
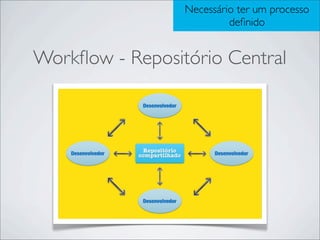
- 7. SVN :: CENTRALIZADO Workflow - Repositório Central
- 8. svn Desenvolvimento Linear Renomear arquivo/pasta dói desvantagens Repos Grandes Resolução de Conflitos ....
- 9. git svn
- 10. “Git is a stupid content tracker.” (Peepcode Git Internals) git
- 11. git != github
- 12. Social Coding Free para projetos Open Source http://www.github.com Firewall para “enterprise”
- 13. Ágil git Autonomia vantagens Repositórios Independentes Resolução de conflitos Repositórios Pequenos
- 14. git Quebra de paradigma desvantagens Curva de Aprendizado t Necessário ter um processo definido
- 15. curiosidade The Ruby on Rails Git repository download, which includes the full history of the project – every version of every file, weighs in at around 13M, which is not even twice the size of a single checkout of the project (~9M). The Subversion server repository for the same project is about 115M. Peepcode Git internals página 12
- 17. Necessário ter um processo definido Workflow - Repositório Central
- 18. Necessário ter um processo definido Workflow - Gerente de Integração
- 19. era uma vez ... Você está sentado em sua mesa trabalhando em uma estória. De repente, sua SM chega perto de você e pede para você parar o que você está fazendo, pois foi encontrado um bug show stopper.
- 20. http://www.google.com.br/imgres?start=116&um=1&hl=pt-BR&biw=1280&bih=636&tbm=isch&tbnid=6fTHDZKMmPElhM:&imgrefurl=http://www.clear-lines.com/ blog/post/Automatically-exclude-bin-and-obj-folder-in-Tortoise-SVN.aspx&docid=OHbeiJsJUJ8saM&imgurl=http://www.clear-lines.com/blog/image.axd%253Fpicture %253DAddFiles_thumb.png&w=387&h=433&ei=KgqFT82RBqr40gHv4djbBw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=665&vpy=279&dur=306&hovh=149&hovw=133&tx=122&ty= 109&sig=105001613950035108112&page=6&tbnh=140&tbnw=125&ndsp=23&ved=1t:429,r:9,s:116,i:104
- 22. Comitar as alterações (sem terminar a task) svn Qual o dev que está com o ambiente limpo? Encontrar o bug; Quanto tempo Implementar o fix; Remover as changes anteriores; levaria? Comitar o fix; Voltar alterações da change. Criar branch; Comitar changes; Voltar no trunk; (?) Comitar fix..
- 23. git Criar Branch Colocar changes no ‘stash’ Quanto tempo levaria? Git permite que o desenvolvedor seja mais ágil!
- 24. filosofia Só código que funciona no master Feature Branch (*) “Commit all the fucking time” “Eu não gosto de resolver conflito!” (aleal) (*) http://martinfowler.com/bliki/FeatureBranch.html
- 25. Commit early, Commit often Never Commit broken code
- 27. Configurando e Commit # Configurando conta do usuário; $ git config -‐-‐global user.name "Alberto Leal" $ git config -‐-‐global user.email albertonb@gmail.com $ git config -‐-‐global color.ui auto # Criando estrutura de pastas do projeto e adicionando alguns arquivos; $ mkdir ~/meu_projeto $ cd ~/meu_projeto $ touch README.txt config.txt # Iniciando um repositório git; $ git init Initialized empty Git repository in ~/meu_projeto/.git/
- 28. Configurando e Commit # Interagindo com o repositório criado; $ git status # On branch master # # Initial commit # # Untracked files: # (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) # # README.txt # config.txt nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track) $ git add . $ git status # On branch master # # Initial commit # # Changes to be committed: # (use "git rm -‐-‐cached <file>..." to unstage) # # new file: README.txt # new file: config.txt
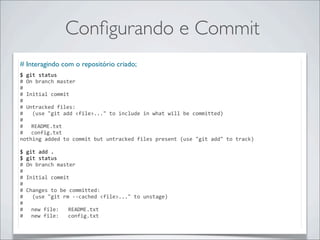
- 29. Configurando e Commit # Criando o primeiro commit; $ git commit -‐m “Initial Commit” [master (root-‐commit) 4692340] Initial Commit 0 files changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-‐) create mode 100644 README.txt create mode 100644 config.txt $ git log commit 4692340f4f326a4120337185474153e65c808cd1 Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Sun Mar 25 19:13:59 2012 -‐0300 Initial Commit
- 30. O que é um commit? Curva de Aprendizado Quebra de paradigma tag v1.0 sha1: 4692340f4f326a4120337185474153e65c808cd1 Commit Tree Blob
- 31. O que é um commit? Curva de Aprendizado Commit Commit (abcde) (fghijl) /public /public index.html index.html whoami.html
- 32. Curva de Aprendizado Working Directory Stage area Repository
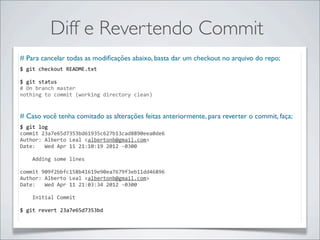
- 33. Diff e Revertendo Commit # Abra o arquivo README.txt e altere o conteúdo; $ git status # On branch master # Changed but not updated: # (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) # (use "git checkout -‐-‐ <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) # # modified: README.txt # no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -‐a") $ git diff diff -‐-‐git a/README.txt b/README.txt index 87147e2..3468b97 100644 -‐-‐-‐ a/README.txt +++ b/README.txt @@ -‐1 +1,3 @@ -‐This is a simple document. No newline at end of file +Este é um documento simples. + +Estamos dando uma olhada no Git. No newline at end of file
- 34. Diff e Revertendo Commit # Para cancelar todas as modificações abaixo, basta dar um checkout no arquivo do repo; $ git checkout README.txt $ git status # On branch master nothing to commit (working directory clean) # Caso você tenha comitado as alterações feitas anteriormente, para reverter o commit, faça; $ git log commit 23a7e65d7353bd61935c627b13cad8890eea0de6 Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Wed Apr 11 21:10:19 2012 -‐0300 Adding some lines commit 909f2bbfc158b41619e90ea7679f3eb11dd46896 Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Wed Apr 11 21:03:34 2012 -‐0300 Initial Commit $ git revert 23a7e65d7353bd
- 35. Diff e Revertendo Commit $ git log commit 143059e977ea838b78c054d37f03a82f82051a7b Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Wed Apr 11 21:11:13 2012 -‐0300 Revert "Adding some lines" This reverts commit 23a7e65d7353bd61935c627b13cad8890eea0de6. commit 23a7e65d7353bd61935c627b13cad8890eea0de6 Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Wed Apr 11 21:10:19 2012 -‐0300 Adding some lines commit 909f2bbfc158b41619e90ea7679f3eb11dd46896 Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Wed Apr 11 21:03:34 2012 -‐0300 Initial Commit
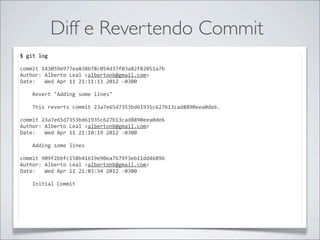
- 36. Criar Branch Branch $ git branch * master $ git branch * master $ git branch new_feature $ git branch * master new_feature $ git checkout -‐b another_feature Switched to a new branch 'another_feature' $ git branch * another_feature master new_feature
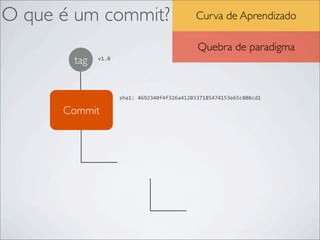
- 37. Criar Branch Branch $ touch a.txt b.txt c.txt d.txt e.txt $ git status # On branch another_feature # Untracked files: # (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) # # a.txt # b.txt # c.txt # d.txt # e.txt nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track) $ git add . && git commit -‐m "Adding new files" [another_feature 08f9fbe] Adding new files 0 files changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-‐) create mode 100644 a.txt create mode 100644 b.txt create mode 100644 c.txt create mode 100644 d.txt create mode 100644 e.txt $ git checkout new_feature $ ls README alberto.txt oi.txt ola.txt
- 38. lembra ...? Você está sentado em sua mesa trabalhando em uma estória. De repente, sua SM chega perto de você e pede para você parar o que você está fazendo, pois foi encontrado um bug show stopper.
- 39. Colocar changes no ‘stash’ Stash $ git checkout another_feature $ ls README alberto.txt c.txt e.txt ola.txt a.txt b.txt d.txt oi.txt $ git status # On branch another_feature # Changed but not updated: # (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) # (use "git checkout -‐-‐ <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) # # modified: a.txt # modified: b.txt # modified: c.txt # modified: d.txt # modified: e.txt # no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -‐a") $ git stash save login_with_ajax Saved working directory and index state On another_feature: login_with_ajax HEAD is now at 08f9fbe Adding new files $ git status # On branch another_feature nothing to commit (working directory clean)
- 40. Colocar changes no ‘stash’ Stash $ git stash list stash@{0}: On another_feature: login_with_ajax $ git stash apply stash@{0} # On branch another_feature # Changed but not updated: # (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) # (use "git checkout -‐-‐ <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) # # modified: a.txt # modified: b.txt # modified: c.txt # modified: d.txt # modified: e.txt # no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -‐a")
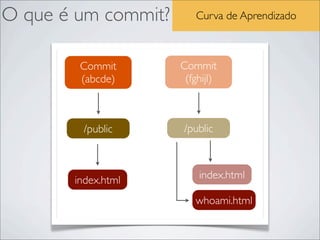
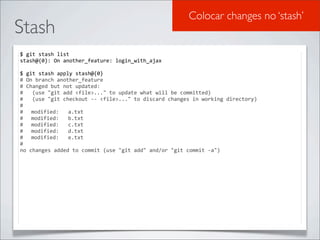
- 41. Resolução de conflitos Resolvendo conflitos $ git checkout master $ git status # On branch master nothing to commit (working directory clean) $ touch a.txt && echo "Workshop de Git" > a.txt $ git add . $ git commit -‐m “Adding new file a” [master e88ac64] Adding file ad 1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-‐) create mode 100644 a.txt $ git checkout another_feature Switched to a new branch 'another_feature' $ echo "CI&T apresenta Workshop de Git" > a.txt $ git commit -‐am "Changing on file a" [another_feature d7a6544] Changing on file a 1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-‐) $ git checkout master Switched to branch 'master'
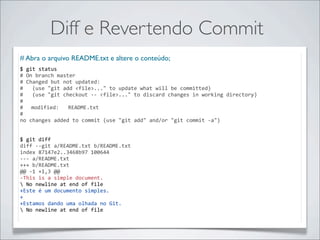
- 42. Resolução de conflitos Resolvendo conflitos $ git merge another_feature Auto-‐merging a.txt CONFLICT (add/add): Merge conflict in a.txt Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result. $ git diff diff -‐-‐cc a.txt index f4e2830,ae35584..0000000 -‐-‐-‐ a/a.txt +++ b/a.txt @@@ -‐1,1 -‐1,1 +1,5 @@@ -‐ Workshop de Git -‐Cit apresenta workshop de git. ++<<<<<<< HEAD ++Workshop de Git ++======= ++Cit apresenta workshop de git. ++>>>>>>> another_feature $ git commit -‐am "Merging branches" [master 36e2a5d] Merging branches $ git log commit 36e2a5d1b4cdc74d967ced02a29190321adefbec Merge: e88ac64 d7a6544 Author: Alberto Leal <albertonb@gmail.com> Date: Wed Apr 11 22:00:50 2012 -‐0300 Merging branches
- 43. Procurando bug com git bisect http://imasters.com.br/artigo/15310/desenvolvimento/git-localizando-a-origem-de-um-bug-atraves-de-busca- binaria-entre-os-commits
- 44. QUEM USA? •Linux Kernel •jQuery •Git •node.js •Perl •Redis •PHP •CakePHP •Eclipse •mongodb •Gnome •... •KDE •Ruby on Rails •Android •PostgreSQL •Debian •X.org
- 46. INSTALANDO GIT Ubuntu sudo apt-get install git-core git-doc git-svn git-gui gitk ssh Windows http://msysgit.github.com/
- 47. OBRIGADO!! aleal@ciandt.com http://www.albertoleal.eti.br/category/git
- 48. adesivos na minha mesa
















![Configurando e Commit
# Criando o primeiro commit;
$
git
commit
-‐m
“Initial
Commit”
[master
(root-‐commit)
4692340]
Initial
Commit
0
files
changed,
0
insertions(+),
0
deletions(-‐)
create
mode
100644
README.txt
create
mode
100644
config.txt
$
git
log
commit
4692340f4f326a4120337185474153e65c808cd1
Author:
Alberto
Leal
<albertonb@gmail.com>
Date:
Sun
Mar
25
19:13:59
2012
-‐0300
Initial
Commit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wokshopgit-2012-120613094443-phpapp02/85/Wokshop-de-Git-29-320.jpg)


![Criar Branch
Branch
$
touch
a.txt
b.txt
c.txt
d.txt
e.txt
$
git
status
#
On
branch
another_feature
#
Untracked
files:
#
(use
"git
add
<file>..."
to
include
in
what
will
be
committed)
#
#
a.txt
#
b.txt
#
c.txt
#
d.txt
#
e.txt
nothing
added
to
commit
but
untracked
files
present
(use
"git
add"
to
track)
$
git
add
.
&&
git
commit
-‐m
"Adding
new
files"
[another_feature
08f9fbe]
Adding
new
files
0
files
changed,
0
insertions(+),
0
deletions(-‐)
create
mode
100644
a.txt
create
mode
100644
b.txt
create
mode
100644
c.txt
create
mode
100644
d.txt
create
mode
100644
e.txt
$
git
checkout
new_feature
$
ls
README
alberto.txt
oi.txt
ola.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wokshopgit-2012-120613094443-phpapp02/85/Wokshop-de-Git-37-320.jpg)


![Resolução de conflitos
Resolvendo conflitos
$
git
checkout
master
$
git
status
#
On
branch
master
nothing
to
commit
(working
directory
clean)
$
touch
a.txt
&&
echo
"Workshop
de
Git"
>
a.txt
$
git
add
.
$
git
commit
-‐m
“Adding
new
file
a”
[master
e88ac64]
Adding
file
ad
1
files
changed,
1
insertions(+),
0
deletions(-‐)
create
mode
100644
a.txt
$
git
checkout
another_feature
Switched
to
a
new
branch
'another_feature'
$
echo
"CI&T
apresenta
Workshop
de
Git"
>
a.txt
$
git
commit
-‐am
"Changing
on
file
a"
[another_feature
d7a6544]
Changing
on
file
a
1
files
changed,
1
insertions(+),
1
deletions(-‐)
$
git
checkout
master
Switched
to
branch
'master'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wokshopgit-2012-120613094443-phpapp02/85/Wokshop-de-Git-41-320.jpg)
![Resolução de conflitos
Resolvendo conflitos
$
git
merge
another_feature
Auto-‐merging
a.txt
CONFLICT
(add/add):
Merge
conflict
in
a.txt
Automatic
merge
failed;
fix
conflicts
and
then
commit
the
result.
$
git
diff
diff
-‐-‐cc
a.txt
index
f4e2830,ae35584..0000000
-‐-‐-‐
a/a.txt
+++
b/a.txt
@@@
-‐1,1
-‐1,1
+1,5
@@@
-‐
Workshop
de
Git
-‐Cit
apresenta
workshop
de
git.
++<<<<<<<
HEAD
++Workshop
de
Git
++=======
++Cit
apresenta
workshop
de
git.
++>>>>>>>
another_feature
$
git
commit
-‐am
"Merging
branches"
[master
36e2a5d]
Merging
branches
$
git
log
commit
36e2a5d1b4cdc74d967ced02a29190321adefbec
Merge:
e88ac64
d7a6544
Author:
Alberto
Leal
<albertonb@gmail.com>
Date:
Wed
Apr
11
22:00:50
2012
-‐0300
Merging
branches](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wokshopgit-2012-120613094443-phpapp02/85/Wokshop-de-Git-42-320.jpg)