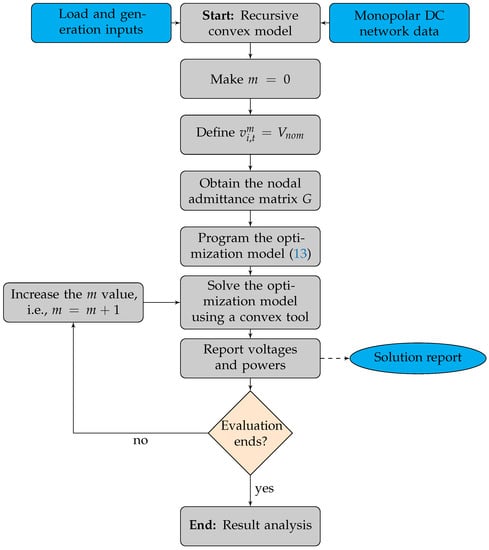
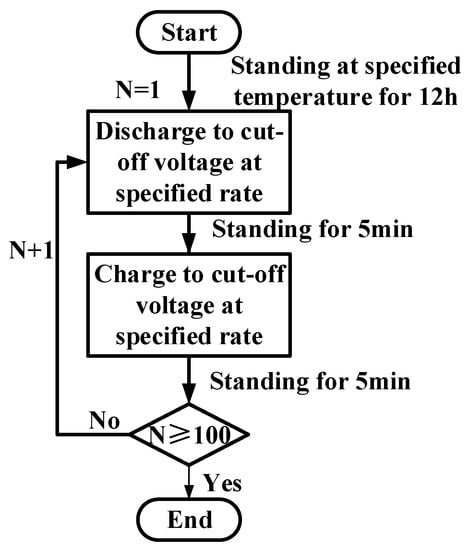
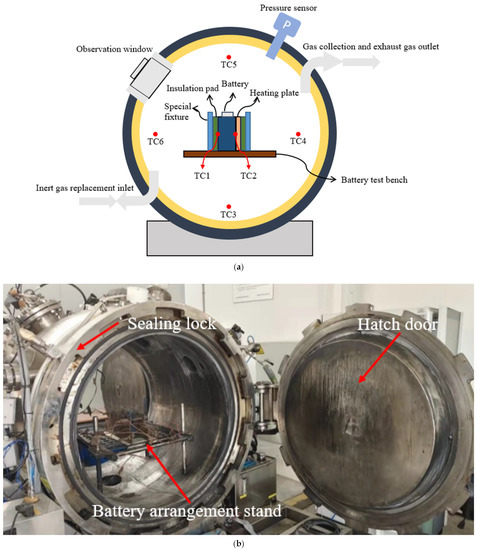
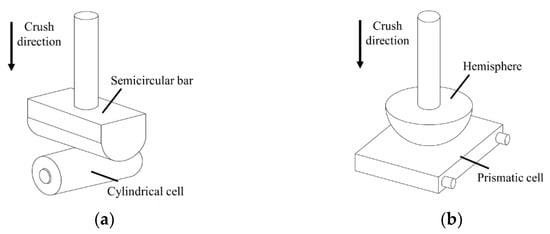
Dear Colleagues,
Currently, the topic of battery energy storage and the applications of batteries is of great interest in the pursuit of a sustainable society. In fact, batteries and their applications are strictly interrelated: the design of new and improved batteries is stimulated by new and improved applications and vice versa. For some applications, batteries with new electrolytes or electrode materials have been specifically realized, while in others, improvements are derived from better energy storage engineering. The aim of this Topical Collection is to update the battery-powered applications and the improvements made through their batteries in terms of technological advancements.
This Topical Collection will include (but not be limited to) the following topics:
- Battery standards;
- Battery safety;
- Battery system design;
- Battery degradation;
- Battery fast charging;
- Battery manufacturing and recycling;
- Advanced battery characterization methods;
- Future batteries, i.e., solid-state batteries, lithium batteries, etc.
Dr. Ottorino Veneri
Dr. Xuning Feng
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Batteries is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Binary Ni/Co Metal-Organic Frameworks as Electrodes for High-Power Energy Storage Applications
Authors: Evangelos I. Gkanas; Ilias Ntoukas; Chiara Milanese; Rong Lan; Alexander Roberts
Affiliation: Centre for Advanced Low Carbon Propulsion Systems (C-ALPS), Coventry University, UK
Abstract: Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are compounds consisting of metal ions coordinated to organic ligands to form crystalline porous structures by self-assembly. They have emerged as a class of crystalline materials with high surface area and porosity, tuneable pore size and functionalized surface. Due tothe metal nodes in the framework, they provide redox centres facilitating faradaic reactions, and due to their crystalline porous structure they provide easier access for electrolyte diffusion. Thus, they own great electrochemical properties, making them ideal for electrode materials for supercapacitors. However, most reported MOFs own an insulating nature which is a major drawback for their electrochemical applications. A common method to solve this restriction is to incorporate another metallic element to enhance the properties of the electrode material. Nickel materials demonstrate high specific capacitance and exhibit promising electrochemical properties as electrode materials for supercapacitors, but they own low rate capability and cycle life, which is attributed to their poor structural stability during the fast charge-discharge process. With the addition of another metal ions such as Co into the structure, more active sites and improved conductivity can be obtained, while stabilizing the Ni species. The partial substitution of the second metal ions in the inorganic nodes will provide synergistic effects for the bimetallic framework. The ratio between the metals can also be adjusted to tune the physiochemical properties of MOFs. In this study, using terephthalic and trimesic acid as the linkers, binary Ni/Co MOFs (Ni:Co = 4:1, 3:1, 2:1, 1:1)have been synthesized utilizing a solvothermal method. Various parameters that affect the structure andproperties of MOFs such as time, temperature, ligands, Ni/Co ratio, and additives have been investigated. Themain focus is on the effect of Co ions that substitute the Ni ones in the framework, how they affect thestructure’s stability and the electrochemical properties of the bimetallic Ni/Co MOFs. These materials have been structurally characterised by SEM, EDX, XRD, XPS, FTIR, TGA, BET and TEM.The morphology consists of 2D interlayered nanosheets with smooth surface that assemble to form 3Dmicroflower-like crystalline structures. The addition of Co leads to a more dense, hierarchical and sphericalmorphology. The phase of these materials is also identified by Rietveld analysis and is: Ni(OH)(CHO) (CCDC no. 985792). The addition of Co does not alter the framework but only provides stability. Moreover, these materials have been electrochemically tested by CV, GCD, EIS and cycling measurements. Alarge specific capacitance of 1503 F/g at 1A/g has been achieved with 70% retention after 3000 cycles. Finally, asymmetric coin cells using these materials and Activated Carbon (AC) have been developed and tested for their capacitance and cycle life.